Page 66 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 66
CHaPTEr 3 Innate Immunity 51
dsRNA-induced activation of RIG-I and MDA-5 induces their TLR2
association with a mitochondria-associated adaptor known as
interferon-β promoter stimulator-1 (IPS-1) or mitochondrial Dectin-1 IL-1β
antiviral signaling protein (MAVS) through CARD domain
interactions. Downstream effectors include TBK-1 and IKKι,
which activate IRF3 and IRF7, leading to production of type-1
interferons (see Fig. 3.6). Of note, live bacteria are more effective
inducers of STAT-1, type I IFN, and inflammasome pathways MyD88 ITAM ITAM
compared with killed organisms, a property that may reflect the Syk
importance of bacterial RNA to innate recognition of live IRAK4
infection. 62 ROI
IRAK1 IRAK2
C-Type Lectin Receptors Raf1 CARD9 MAPKs
C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) are a diverse group of receptors NLRP3
2+
originally identified as Ca -dependent carbohydrate-binding inflammasome
63
proteins. CLRs are defined as any protein that contains a C-type
carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD), regardless of calcium- or NF-κB NFAT AP1 Pro-IL-1β
carbohydrate-binding ability. CLRs include numerous members
with diverse functions, including cell adhesion, regulation of
NK-cell function, phagocytosis, endocytosis, platelet activation,
complement activation, tissue remodeling, and innate immunity. Cytokine gene transcription
In myeloid cells, CLRs can mediate internalization of microbes
to allow for antigen processing and presentation. Some CLRs
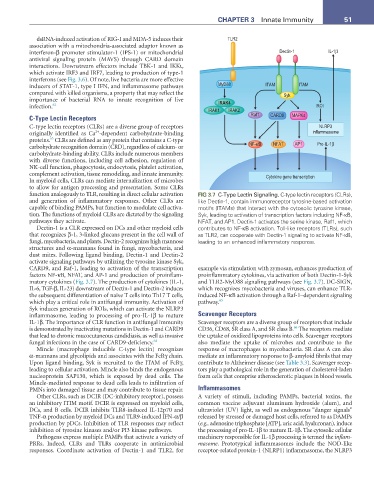
function analogously to TLR, resulting in direct cellular activation FIG 3.7 C-Type Lectin Signaling. C-type lectin receptors (CLRs),
and generation of inflammatory responses. Other CLRs are like Dectin-1, contain immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation
capable of binding PAMPs, but function to modulate cell activa- motifs (ITAMs) that interact with the cytosolic tyrosine kinase,
tion. The functions of myeloid CLRs are dictated by the signaling Syk, leading to activation of transcription factors including NF-κB,
pathways they activate. NFAT, and AP1. Dectin-1 activates the serine kinase, Raf1, which
Dectin-1 is a CLR expressed on DCs and other myeloid cells contributes to NF-κB activation. Toll-like receptors (TLRs), such
that recognizes β-1, 3-linked glucans present in the cell wall of as TLR2, can cooperate with Dectin-1 signaling to activate NF-κB,
fungi, mycobacteria, and plants. Dectin-2 recognizes high mannose leading to an enhanced inflammatory response.
structures and α-mannans found in fungi, mycobacteria, and
dust mites. Following ligand binding, Dectin-1 and Dectin-2
activate signaling pathways by utilizing the tyrosine kinase Syk,
CARD9, and Raf-1, leading to activation of the transcription example via stimulation with zymosan, enhances production of
factors NF-κB, NFAT, and AP-1 and production of proinflam- proinflammatory cytokines, via activation of both Dectin-1-Syk
matory cytokines (Fig. 3.7). The production of cytokines (IL-1, and TLR2-MyD88 signaling pathways (see Fig. 3.7). DC-SIGN,
IL-6, TGF-β, IL-23) downstream of Dectin-1 and Dectin-2 induces which recognizes mycobacteria and viruses, can enhance TLR-
the subsequent differentiation of naïve T cells into Th17 T cells, induced NF-κB activation through a Raf-1–dependent signaling
which play a critical role in antifungal immunity. Activation of pathway. 65
Syk induces generation of ROIs, which can activate the NLRP3
inflammasome, leading to processing of pro-IL-1β to mature Scavenger Receptors
IL-1β. The importance of CLR function in antifungal immunity Scavenger receptors are a diverse group of receptors that include
66
is demonstrated by inactivating mutations in Dectin-1 and CARD9 CD36, CD68, SR class A, and SR class B. The receptors mediate
that lead to chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, as well as invasive the uptake of oxidized lipoproteins into cells. Scavenger receptors
fungal infections in the case of CARD9-deficiency. 64 also mediate the uptake of microbes and contribute to the
Mincle (macrophage inducible C-type lectin) recognizes response of macrophages to mycobacteria. SR class A can also
α-mannans and glycolipids and associates with the FcRγ chain. mediate an inflammatory response to β-amyloid fibrils that may
Upon ligand binding, Syk is recruited to the ITAM of FcRγ, contribute to Alzheimer disease (see Table 3.3). Scavenger recep-
leading to cellular activation. Mincle also binds the endogenous tors play a pathological role in the generation of cholesterol-laden
nucleoprotein SAP130, which is exposed by dead cells. The foam cells that comprise atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels.
Mincle-mediated response to dead cells leads to infiltration of
PMNs into damaged tissue and may contribute to tissue repair. Inflammasomes
Other CLRs, such as DCIR (DC-inhibitory receptor), possess A variety of stimuli, including PAMPs, bacterial toxins, the
an inhibitory ITIM motif. DCIR is expressed on myeloid cells, common vaccine adjuvant aluminum hydroxide (alum), and
DCs, and B cells. DCIR inhibits TLR8-induced IL-12p70 and ultraviolet (UV) light, as well as endogenous “danger signals”
TNF-α production by myeloid DCs and TLR9-induced IFN-α/β released by stressed or damaged host cells, referred to as DAMPs
production by pDCs. Inhibition of TLR responses may reflect (e.g., adenosine triphosphate [ATP], uric acid, hyaluronan), induce
inhibition of tyrosine kinases and/or PI3 kinase pathways. the processing of pro-IL-1β to mature IL-1β. The cytosolic cellular
Pathogens express multiple PAMPs that activate a variety of machinery responsible for IL-1β processing is termed the inflam-
PRRs. Indeed, CLRs and TLRs cooperate in antimicrobial masome. Prototypical inflammasomes include the NOD-like
responses. Coordinate activation of Dectin-1 and TLR2, for receptor-related protein-1 (NLRP1) inflammasome, the NLRP3