Page 857 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 857
828 ParT SIX Systemic Immune Diseases
TABLE 60.2 Diagnostic Criteria for NLRP3
Schnitzler Syndrome a LRR NOD PYD
Major Criteria (≥1 present) FIIND PYD CARD ASC
(Chronic) urticarial rash
Monoclonal immunoglobulin M (IgM; or IgG: variant type) CARD CARD Pro-caspase-1
CARD
Minor Criteria (≥2 present) Caspase-1
Intermittent fever Caspase-1
Arthralgia or arthritis
Bone pain
Lymphadenopathy Pro-
Hepatomegaly and/or splenomegaly IL-1β IL-1β
Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and/or leukocytosis
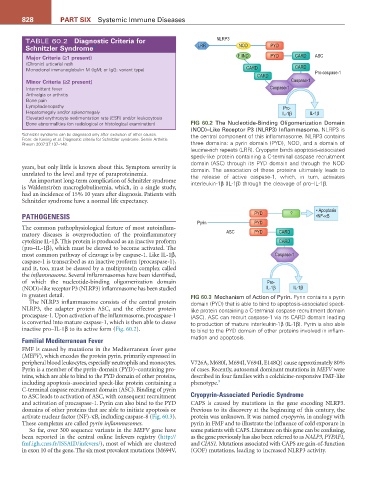
Bone abnormalities (on radiological or histological examination) FIG 60.2 The Nucleotide-Binding Oligomerization Domain
(NOD)–Like Receptor P3 (NLRP3) Inflammasome. NLRP3 is
a Schnizler syndrome can be diagnosed only after exclusion of other causes. the central component of this inflammasome. NLRP3 contains
From: de Koning et al. Diagnostic criteria for Schnitzler syndrome. Semin Arthritis
Rheum 2007:37:137–148. three domains: a pyrin domain (PYD), NOD, and a domain of
leucine-rich repeats (LRR). Cryopyrin binds apoptosis-associated
speck-like protein containing a C-terminal caspase recruitment
domain (ASC) through its PYD domain and through the NOD
years, but only little is known about this. Symptom severity is domain. The association of these proteins ultimately leads to
unrelated to the level and type of paraproteinemia. the release of active caspase-1, which, in turn, activates
An important long-term complication of Schnitzler syndrome interleukin-1β (IL-1β) through the cleavage of pro–IL-1β.
is Waldenström macroglobulinemia, which, in a single study,
had an incidence of 15% 10 years after diagnosis. Patients with
Schnitzler syndrome have a normal life expectancy.
• Apoptosis
PATHOGENESIS PYD ? •NF-κB
Pyrin PYD
The common pathophysiological feature of most autoinflam-
matory diseases is overproduction of the proinflammatory ASC PYD CARD
cytokine IL-1β. This protein is produced as an inactive proform CARD
(pro–IL-1β), which must be cleaved to become activated. The
most common pathway of cleavage is by caspase-1. Like IL-1β, Caspase-1
caspase-1 is transcribed as an inactive proform (procaspase-1),
and it, too, must be cleaved by a multiprotein complex called
the inflammasome. Several inflammasomes have been identified,
of which the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain Pro-
(NOD)–like receptor P3 (NLRP3) inflammasome has been studied IL-1β IL-1β
in greatest detail. FIG 60.3 Mechanism of Action of Pyrin. Pyrin contains a pyrin
The NLRP3 inflammasome consists of the central protein domain (PYD) that is able to bind to apoptosis-associated speck-
NLRP3, the adapter protein ASC, and the effector protein like protein containing a C-terminal caspase recruitment domain
procaspase-1. Upon activation of the inflammasome, procaspase-1 (ASC). ASC can recruit caspase-1 via its CARD domain leading
is converted into mature caspase-1, which is then able to cleave to production of mature interleukin-1β (IL-1β). Pyrin is also able
inactive pro–IL-1β to its active form (Fig. 60.2). to bind to the PYD domain of other proteins involved in inflam-
Familial Mediterranean Fever mation and apoptosis.
FMF is caused by mutations in the Mediterranean fever gene
(MEFV), which encodes the protein pyrin, primarily expressed in
peripheral blood leukocytes, especially neutrophils and monocytes. V726A, M680I, M694I, V694I, E148Q) cause approximately 80%
Pyrin is a member of the pyrin-domain (PYD)–containing pro- of cases. Recently, autosomal dominant mutations in MEFV were
teins, which are able to bind to the PYD domain of other proteins, described in four families with a colchicine-responsive FMF-like
including apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a phenotype. 9
C-terminal caspase recruitment domain (ASC). Binding of pyrin
to ASC leads to activation of ASC, with consequent recruitment Cryopyrin-Associated Periodic Syndrome
and activation of procaspase-1. Pyrin can also bind to the PYD CAPS is caused by mutations in the gene encoding NLRP3.
domains of other proteins that are able to initiate apoptosis or Previous to its discovery at the beginning of this century, the
activate nuclear factor (NF)-κB, including caspase-8 (Fig. 60.3). protein was unknown. It was named cryopyrin, in analogy with
These complexes are called pyrin inflammasomes. pyrin in FMF and to illustrate the influence of cold exposure in
So far, over 300 sequence variants in the MEFV gene have some patients with CAPS. Literature on this gene can be confusing,
been reported in the central online Infevers registry (http:// as the gene previously has also been referred to as NALP3, PYPAF1,
fmf.igh.cnrs.fr/ISSAID/infevers/), most of which are clustered and CIAS1. Mutations associated with CAPS are gain-of-function
in exon 10 of the gene. The six most prevalent mutations (M694V, (GOF) mutations, leading to increased NLRP3 activity.