Page 961 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 961
928 Part Seven Organ-Specific Inflammatory Disease
$ %
& '
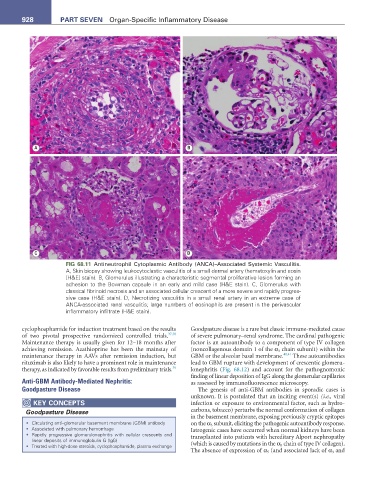
FIG 68.11 Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)–Associated Systemic Vasculitis.
A, Skin biopsy showing leukocytoclastic vasculitis of a small dermal artery (hematoxylin and eosin
[H&E] stain). B, Glomerulus illustrating a characteristic segmental proliferative lesion forming an
adhesion to the Bowman capsule in an early and mild case (H&E stain). C, Glomerulus with
classical fibrinoid necrosis and an associated cellular crescent of a more severe and rapidly progres-
sive case (H&E stain). D, Necrotizing vasculitis in a small renal artery in an extreme case of
ANCA-associated renal vasculitis; large numbers of eosinophils are present in the perivascular
inflammatory infiltrate (H&E stain).
cyclophosphamide for induction treatment based on the results Goodpasture disease is a rare but classic immune-mediated cause
of two pivotal prospective randomized controlled trials. 37,38 of severe pulmonary–renal syndrome. The cardinal pathogenic
Maintenance therapy is usually given for 12–18 months after factor is an autoantibody to a component of type IV collagen
achieving remission. Azathioprine has been the mainstay of (noncollagenous domain 1 of the α 3 chain subunit) within the
maintenance therapy in AAVs after remission induction, but GBM or the alveolar basal membrane. 40,41 These autoantibodies
rituximab is also likely to have a prominent role in maintenance lead to GBM rupture with development of crescentic glomeru-
therapy, as indicated by favorable results from preliminary trials. 39 lonephritis (Fig. 68.12) and account for the pathognomonic
finding of linear deposition of IgG along the glomerular capillaries
Anti-GBM Antibody-Mediated Nephritis: as assessed by immunofluorescence microscopy.
Goodpasture Disease The genesis of anti-GBM antibodies in sporadic cases is
unknown. It is postulated that an inciting event(s) (i.e., viral
KeY COnCePtS infection or exposure to environmental factor, such as hydro-
Goodpasture Disease carbons, tobacco) perturbs the normal conformation of collagen
in the basement membrane, exposing previously cryptic epitopes
• Circulating anti–glomerular basement membrane (GBM) antibody on the α 3 subunit, eliciting the pathogenic autoantibody response.
• Associated with pulmonary hemorrhage Iatrogenic cases have occurred when normal kidneys have been
• Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis with cellular crescents and transplanted into patients with hereditary Alport nephropathy
linear deposits of immunoglobulin G (IgG)
• Treated with high-dose steroids, cyclophosphamide, plasma exchange (which is caused by mutations in the α 5 chain of type IV collagen).
The absence of expression of α 5 (and associated lack of α 3 and