Page 959 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 959
926 Part Seven Organ-Specific Inflammatory Disease
$ %
& '
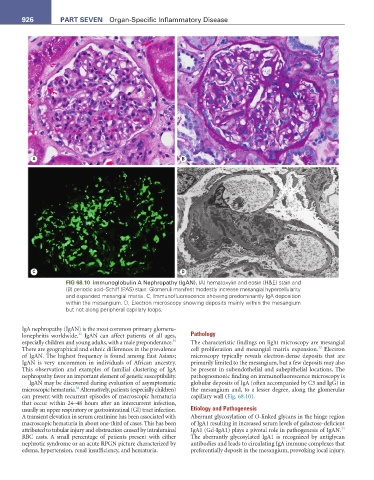
FIG 68.10 Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy (IgAN). (A) hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain and
(B) periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) stain: Glomeruli manifest modestly increase mesangial hypercellularity
and expanded mesangial matrix. C, Immunofluorescence showing predominantly IgA deposition
within the mesangium. D, Electron microscopy showing deposits mainly within the mesangium
but not along peripheral capillary loops.
IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is the most common primary glomeru-
32
lonephritis worldwide. IgAN can affect patients of all ages, Pathology
34
especially children and young adults, with a male preponderance. The characteristic findings on light microscopy are mesangial
32
There are geographical and ethnic differences in the prevalence cell proliferation and mesangial matrix expansion. Electron
of IgAN. The highest frequency is found among East Asians; microscopy typically reveals electron-dense deposits that are
IgAN is very uncommon in individuals of African ancestry. primarily limited to the mesangium, but a few deposits may also
This observation and examples of familial clustering of IgA be present in subendothelial and subepithelial locations. The
nephropathy favor an important element of genetic susceptibility. pathognomonic finding on immunofluorescence microscopy is
IgAN may be discovered during evaluation of asymptomatic globular deposits of IgA (often accompanied by C3 and IgG) in
34
microscopic hematuria. Alternatively, patients (especially children) the mesangium and, to a lesser degree, along the glomerular
can present with recurrent episodes of macroscopic hematuria capillary wall (Fig. 68.10).
that occur within 24–48 hours after an intercurrent infection,
usually an upper respiratory or gastrointestinal (GI) tract infection. Etiology and Pathogenesis
A transient elevation in serum creatinine has been associated with Aberrant glycosylation of O-linked glycans in the hinge region
macroscopic hematuria in about one-third of cases. This has been of IgA1 resulting in increased serum levels of galactose-deficient
34
attributed to tubular injury and obstruction caused by intraluminal IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) plays a pivotal role in pathogenesis of IgAN.
RBC casts. A small percentage of patients present with either The aberrantly glycosylated IgA1 is recognized by antiglycan
nephrotic syndrome or an acute RPGN picture characterized by antibodies and leads to circulating IgA immune complexes that
edema, hypertension, renal insufficiency, and hematuria. preferentially deposit in the mesangium, provoking local injury.