Page 1350 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1350
CHAPTER 97: Acute Kidney Injury 923
120 independent of GFR in studies to date. 77-79 It undergoes purely renal
Surgery, MI, sepsis excretion. Serum cystatin C levels increase before serum creatinine
100 levels in patients with progressive chronic kidney disease. 77,79 Emerging
GFR (mL/min) 80 Reversal of ischemia data suggest that plasma cystatin C levels similarly increase 1 to 2 days
60
before serum creatinine in patients developing AKI in a variety of
settings, including radio-contrast nephropathy, renal transplantation,
80
81,82
79
40
84
83
20 cirrhotic AKI, malarial AKI, and AKI in the ICU. 85,86 In the latter study
of 85 critically ill patients, Herget-Rosenthal and colleagues showed that
0 7 6 AKI defined by elevation of cystatin C occurred 1 to 2 days before serum
Serum creatinine (mg%) 5 4 3 2 analysis was 0.82 and 0.97 on the 2 days prior to creatinine-defined AKI. 86
creatinine elevation; the area under the curve in receiver operating curve
In patients with azotemia and/or oliguria, traditional urine chemistry
markers may provide useful information, interpreted in combination with
other clinical and laboratory parameters (see below), including micro-
hypoperfusion and injury will prove clinically useful in the future.
88,89
0 1 scopic urinalysis. 72,87 Hopefully, more sensitive markers of early renal
0 7 14 21 28 Meanwhile, all clinically available renal function indices should be used
Time, days in combination for assessment of renal perfusion and function in the ICU.
FIGURE 97-3. Dynamic relationship between serum creatinine and GFR in AKI. Moran and ■ DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH TO ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Myers demonstrated that elevation of serum creatinine lags significantly behind GFR decre-
ments in AKI. In this example, an acute decrement in GFR to <10 mL/min (commonly a dialysis- The diagnostic approach to AKI involves assignment of the cause to
requiring level) after a major ischemic insult is associated with a subsequent slow, daily rise of prerenal, renal, or postrenal categories, with further refinement of the
serum creatinine. The daily serum creatinine increment is determined by creatinine generation diagnosis based on additional laboratory testing.
(muscle mass and catabolic state), volume status (volume of distribution of creatinine), and the History and Physical Examination in Acute Renal Failure: Any decrease in
new GFR level. Serum creatinine continues to rise until creatinine generation equals creatinine effective perfusion of the kidneys can result in the syndrome of prer-
excretion at steady state. Only after a week is it fully apparent from the serum creatinine level enal AKI. This may be the result of an absolute decrease in the extra-
how low the GFR is in this patient with AKI; this could have been inferred from the progressive cellular fluid (ECF) volume, redistribution of ECF from vascular to
daily serum creatinine increments, and measured by urine collection for an abbreviated creati- interstitial locations (third-spacing), or impaired delivery of blood
nine clearance. (Reproduced with permission from Moran SM, Myers BD. Course of acute renal to the kidneys such as can occur in patients with renal arterial ste-
failure studied by a model of creatinine kinetics. Kidney Int. June 1985;27(6):928-937.) nosis, vasculitis, or depressed cardiac function. Third-space losses
should be suspected in the presence of severe burns, pancreatitis,
estimate of GFR than serum creatinine alone, and are more timely than peritonitis, or recent abdominal surgery. Absolute decreases in the
24-hour urine collections. Emerging data suggest that serial monitoring ECF volume are most common in the setting of gastrointestinal fluid
76
of serum cystatin C levels may provide a more sensitive index of early losses or in patients receiving excessive doses of diuretics.
AKI than serum creatinine or BUN. Cystatin C is a nonglycosylated Decreases in weight, if known, can provide some information
13-kDa basic protein that is a member of the cystatin super-family of about the degree of ECF loss. However, weight changes are subject to
cysteine protease inhibitors. It is produced by all nucleated cells, and misinterpretation if the nature of fluid loss is not taken into account
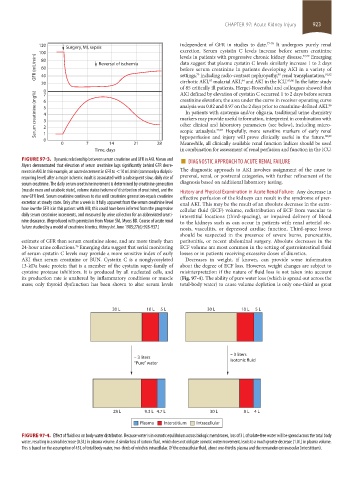
its production rate is unaltered by inflammatory conditions or muscle (Fig. 97-4). The ability of pure water loss (which is spread out across the
mass; only thyroid dysfunction has been shown to alter serum levels total-body water) to cause volume depletion is only one-third as great
30 L 10 L 5 L 30 L 10 L 5 L
– 3 liters
– 3 liters isotonic fluid
“Pure” water
28 L 9.3 L 4.7 L 30 L 8 L 4 L
Plasma Interstitium Intracellular
FIGURE 97-4. Effect of fluid loss on body water distribution. Because water is in osmotic equilibrium across biologic membranes, loss of 3 L of solute-free water will be spread across the total body
water, resulting in a small decrease (0.3 L) in plasma volume. A similar loss of isotonic fluid, which does not obligate osmotic water movement, leads to a much greater decrease (1.0 L) in plasma volume.
This is based on the assumption of 45 L of total body water, two-thirds of which is intracellular. Of the extracellular fluid, about one-third is plasma and the remainder extravascular (interstitium).
section08.indd 923 1/14/2015 8:27:55 AM