Page 246 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 246
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Picornaviruses (+) RNA (±) DNA Papovaviruses (+) DNA or (–) DNA mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 29 Replication
235
Adenoviruses
Herpesviruses
Hepadnaviruses*
Poxviruses*
(±) DNA
Togaviruses
Parvoviruses
Flaviviruses
Viral
Paramyxoviruses*
(+) RNA (±) DNA (+) mRNA (–) RNA Orthomyxoviruses*
mebooksfree.com
Retroviruses*
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com (+) = Strand with same polarity as mRNA (±) = Double-stranded mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Rhabdoviruses*
mebooksfree.com
(±) RNA
Reoviruses*
Legend:
(–) = Strand complementary to mRNA
= These viruses contain a polymerase in the virion
*
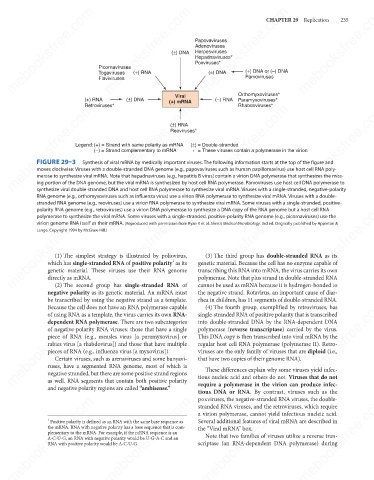
FIGURE 29–3
Synthesis of viral mRNA by medically important viruses. The following information starts at the top of the figure and
moves clockwise: Viruses with a double-stranded DNA genome (e.g., papovaviruses such as human papillomavirus) use host cell RNA poly-
merase to synthesize viral mRNA. Note that hepadnaviruses (e.g., hepatitis B virus) contain a virion DNA polymerase that synthesizes the miss-
ing portion of the DNA genome, but the viral mRNA is synthesized by host cell RNA polymerase. Parvoviruses use host cell DNA polymerase to
synthesize viral double-stranded DNA and host cell RNA polymerase to synthesize viral mRNA. Viruses with a single-stranded, negative-polarity
RNA genome (e.g., orthomyxoviruses such as influenza virus) use a virion RNA polymerase to synthesize viral mRNA. Viruses with a double-
stranded RNA genome (e.g., reoviruses) use a virion RNA polymerase to synthesize viral mRNA. Some viruses with a single-stranded, positive-
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com genetic material. Because the cell has no enzyme capable of mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
polarity RNA genome (e.g., retroviruses) use a virion DNA polymerase to synthesize a DNA copy of the RNA genome but a host cell RNA
polymerase to synthesize the viral mRNA. Some viruses with a single-stranded, positive-polarity RNA genome (e.g., picornaviruses) use the
virion genome RNA itself as their mRNA. (Reproduced with permission from Ryan K et al. Sherris Medical Microbiology. 3rd ed. Originally published by Appleton &
Lange. Copyright 1994 by McGraw-Hill.)
(1) The simplest strategy is illustrated by poliovirus,
(3) The third group has double-stranded RNA as its
1
which has single-stranded RNA of positive polarity as its
genetic material. These viruses use their RNA genome
directly as mRNA.
polymerase. Note that plus strand in double-stranded RNA
cannot be used as mRNA because it is hydrogen-bonded to
(2) The second group has single-stranded RNA of
the negative strand. Rotavirus, an important cause of diar-
negative polarity as its genetic material. An mRNA must transcribing this RNA into mRNA, the virus carries its own
be transcribed by using the negative strand as a template.
rhea in children, has 11 segments of double-stranded RNA.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com into double-stranded DNA by the RNA-dependent DNA mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Because the cell does not have an RNA polymerase capable
(4) The fourth group, exemplified by retroviruses, has
single-stranded RNA of positive polarity that is transcribed
of using RNA as a template, the virus carries its own RNA-
dependent RNA polymerase. There are two subcategories
of negative-polarity RNA viruses: those that have a single
polymerase (reverse transcriptase) carried by the virus.
piece of RNA (e.g., measles virus [a paramyxovirus] or
This DNA copy is then transcribed into viral mRNA by the
rabies virus [a rhabdovirus]) and those that have multiple
regular host cell RNA polymerase (polymerase II). Retro-
pieces of RNA (e.g., influenza virus [a myxovirus]).
viruses are the only family of viruses that are diploid (i.e.,
that have two copies of their genome RNA).
Certain viruses, such as arenaviruses and some bunyavi-
ruses, have a segmented RNA genome, most of which is
These differences explain why some viruses yield infec-
negative stranded, but there are some positive strand regions
tious nucleic acid and others do not. Viruses that do not
as well. RNA segments that contain both positive polarity
require a polymerase in the virion can produce infec-
and negative polarity regions are called “ambisense.”
tious DNA or RNA. By contrast, viruses such as the
mebooksfree.com
poxviruses, the negative-stranded RNA viruses, the double-
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Several additional features of viral mRNA are described in mebooksfree.com
stranded RNA viruses, and the retroviruses, which require
a virion polymerase, cannot yield infectious nucleic acid.
1
Positive polarity is defined as an RNA with the same base sequence as
the mRNA. RNA with negative polarity has a base sequence that is com-
the “Viral mRNA” box.
plementary to the mRNA. For example, if the mRNA sequence is an
Note that two families of viruses utilize a reverse tran-
A-C-U-G, an RNA with negative polarity would be U-G-A-C and an
scriptase (an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase) during
RNA with positive polarity would be A-C-U-G.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com