Page 250 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 250
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Nature of Polyprotein Site of Proteolytic Medically Important Viruses 239 mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 29 Replication
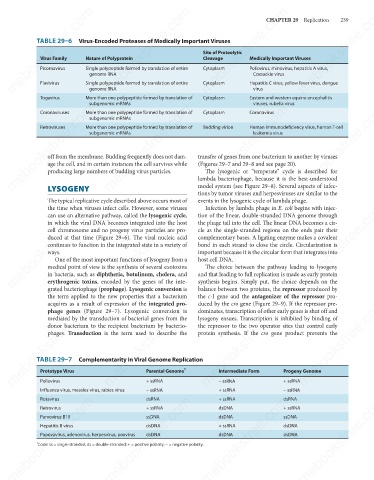
TABLE 29–6 Virus-Encoded Proteases of Medically Important Viruses
Virus Family
Cleavage
Single polypeptide formed by translation of entire
Cytoplasm
Poliovirus, rhinovirus, hepatitis A virus,
Picornavirus
Coxsackie virus
genome RNA
Flavivirus
genome RNA
virus
More than one polypeptide formed by translation of
Cytoplasm
Togavirus Single polypeptide formed by translation of entire Cytoplasm Hepatitis C virus, yellow fever virus, dengue
Eastern and western equine encephalitis
subgenomic mRNAs
viruses, rubella virus
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com More than one polypeptide formed by translation of transfer of genes from one bacterium to another by viruses mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Cytoplasm
Coronavirus
More than one polypeptide formed by translation of
Coronaviruses
subgenomic mRNAs
Budding virion
Human immunodeficiency virus, human T-cell
Retroviruses
leukemia virus
subgenomic mRNAs
off from the membrane. Budding frequently does not dam-
(Figures 29–7 and 29–8 and see page 20).
age the cell, and in certain instances the cell survives while
The lysogenic or “temperate” cycle is described for
producing large numbers of budding virus particles.
lambda bacteriophage, because it is the best-understood
model system (see Figure 29–8). Several aspects of infec-
LYSOGENY
tions by tumor viruses and herpesviruses are similar to the
The typical replicative cycle described above occurs most of
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com events in the lysogenic cycle of lambda phage. mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Infection by lambda phage in E. coli begins with injec-
the time when viruses infect cells. However, some viruses
tion of the linear, double-stranded DNA genome through
can use an alternative pathway, called the lysogenic cycle,
the phage tail into the cell. The linear DNA becomes a cir-
in which the viral DNA becomes integrated into the host
cle as the single-stranded regions on the ends pair their
cell chromosome and no progeny virus particles are pro-
complementary bases. A ligating enzyme makes a covalent
duced at that time (Figure 29–6). The viral nucleic acid
continues to function in the integrated state in a variety of
bond in each strand to close the circle. Circularization is
ways.
important because it is the circular form that integrates into
One of the most important functions of lysogeny from a
host cell DNA.
medical point of view is the synthesis of several exotoxins
The choice between the pathway leading to lysogeny
in bacteria, such as diphtheria, botulinum, cholera, and
synthesis begins. Simply put, the choice depends on the
erythrogenic toxins, encoded by the genes of the inte-
balance between two proteins, the repressor produced by
grated bacteriophage (prophage). Lysogenic conversion is
the c-I gene and the antagonizer of the repressor pro-
the term applied to the new properties that a bacterium and that leading to full replication is made as early protein
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com the repressor to the two operator sites that control early mebooksfree.com
acquires as a result of expression of the integrated pro-
duced by the cro gene (Figure 29–9). If the repressor pre-
dominates, transcription of other early genes is shut off and
phage genes (Figure 29–7). Lysogenic conversion is
mediated by the transduction of bacterial genes from the
lysogeny ensues. Transcription is inhibited by binding of
donor bacterium to the recipient bacterium by bacterio-
protein synthesis. If the cro gene product prevents the
phages. Transduction is the term used to describe the
TABLE 29–7 Complementarity in Viral Genome Replication
Prototype Virus
- ssRNA
+ ssRNA
Poliovirus
+ ssRNA
- ssRNA
Influenza virus, measles virus, rabies virus Parental Genome 1 Intermediate Form Progeny Genome
- ssRNA
+ ssRNA
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com ssDNA mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
dsRNA
+ ssRNA
dsRNA
Rotavirus
+ ssRNA
+ ssRNA
Retrovirus
dsDNA
Parvovirus B19
dsDNA
ssDNA
dsDNA
Hepatitis B virus
+ ssRNA
dsDNA
dsDNA
dsDNA
dsDNA
Papovavirus, adenovirus, herpesvirus, poxvirus
1
Code: ss = single-stranded; ds = double-stranded; + = positive polarity; - = negative polarity.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com