Page 53 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 53
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Organism Mode of Action Exotoxin mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
42
PART I Basic Bacteriology
TABLE 7–13 Main Location of Symptoms of Disease Caused by Bacterial Exotoxins
Main Location of
Symptoms
Gastrointestinal tract
Inactivates GTPases in enterocytes
Clostridium difficile
2. Gram-positive rods
Superantigen
Clostridium perfringens
Superantigen
Bacillus cereus
1. Gram-positive cocci Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxin is a superantigen
Stimulates adenylate cyclase
Vibrio cholerae
3. Gram-negative rods
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Clostridium tetani Inhibits glycine release mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Toxigenic Escherichia coli
Stimulates adenylate cyclase
Escherichia coli O157
Inactivates protein synthesis
Nervous system
1. Gram-positive rods
Inhibits acetylcholine release
Clostridium botulinum
Respiratory tract
Inactivates protein synthesis
1. Gram-positive rods
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Stimulates adenylate cyclase; inhibits chemokine receptor
2. Gram-negative rods
Bordetella pertussis
1. Gram-positive cocci
S. aureus (MRSA strains)
PV leukocidin is a pore-forming toxin that disrupts cell membrane
Skin, soft tissue, or muscle S. aureus (scalded skin syndrome) Protease cleaves desmosome in skin
Streptococcus pyogenes (scarlet fever)
Erythrogenic toxin is a superantigen
Lecithinase cleaves cell membranes
2. Gram-positive rods
C. perfringens
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com S. aureus is a protease that degrades the protein(s) responsible for the mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Bacillus anthracis
Edema factor is an adenylate cyclase; lethal factor is a protease
Systemic
Toxic shock syndrome toxin is a superantigen
1. Gram-positive cocci
MRSA = methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; PV = Panton-Valentine.
may travel either by retrograde axonal transport or in the
bloodstream to the anterior horn and interstitial neurons of
release of acetylcholine. There are six serotypes of botuli-
the spinal cord. Blockage of release of the inhibitory trans-
plasmid, some on a temperate bacteriophage, and some on
mitter leads to convulsive contractions of the voluntary
the bacterial chromosome.
muscles, best exemplified by spasm of the jaw and neck
muscles (“lockjaw”). num toxin (A–F). Some serotypes are encoded on a
(4) Two exotoxins are produced by Clostridium difficile,
(3) Botulinum toxin, produced by Clostridium botulinum,
both of which are involved in the pathogenesis of pseudo-
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com ages the colonic mucosa and causes pseudomembranes to mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
membranous colitis. Exotoxin A is an enterotoxin that
is a neurotoxin that blocks the release of acetylcholine at
causes watery diarrhea. Exotoxin B is a cytotoxin that dam-
the synapse, producing a flaccid paralysis. Approximately 1
μg is lethal for humans; it is one of the most toxic com-
form. Exotoxins A and B are glucosyltransferases that glu-
pounds known. The toxin is composed of two polypeptide
subunits held together by disulfide bonds. One of the sub-
cosylate signal transduction proteins called Rho GTPases—
a process that inhibits these GTPases from performing
units binds to a receptor on the neuron; the other subunit
–
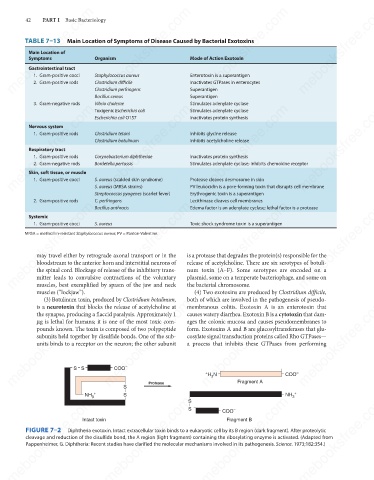
S
COO
S
3
NH 3 + S Protease S + H N COO – Fragment A C O 3 O + –
S
NH
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
S
Fragment B
Intact toxin
FIGURE 7–2
Diphtheria exotoxin. Intact extracellular toxin binds to a eukaryotic cell by its B region (dark fragment). After proteolytic
cleavage and reduction of the disulfide bond, the A region (light fragment) containing the ribosylating enzyme is activated. (Adapted from
Pappenheimer, G. Diphtheria: Recent studies have clarified the molecular mechanisms involved in its pathogenesis. Science. 1973;182:354.)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com