Page 55 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 55
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Active subunit ADP-R cAMP mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
PART I Basic Bacteriology
44
ENTEROCYTE
Water and
Protein
electrolytes
kinase
Cholera
toxin
Binding subunit
G
Adenylate
s
cyclase
protein
bicarbonate
GUT LUMEN Water, chloride,
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com receptors. This causes the marked lymphocytosis seen in mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Diarrhea
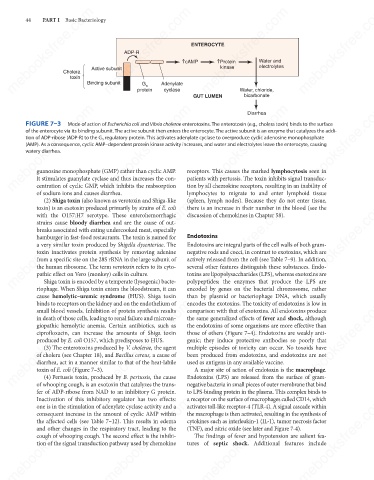
FIGURE 7–3
Mode of action of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae enterotoxins. The enterotoxin (e.g., cholera toxin) binds to the surface
of the enterocyte via its binding subunit. The active subunit then enters the enterocyte. The active subunit is an enzyme that catalyzes the addi-
tion of ADP-ribose (ADP-R) to the G S regulatory protein. This activates adenylate cyclase to overproduce cyclic adenosine monophosphate
(AMP). As a consequence, cyclic AMP–dependent protein kinase activity increases, and water and electrolytes leave the enterocyte, causing
watery diarrhea.
guanosine monophosphate (GMP) rather than cyclic AMP.
It stimulates guanylate cyclase and thus increases the con-
centration of cyclic GMP, which inhibits the reabsorption
tion by all chemokine receptors, resulting in an inability of
of sodium ions and causes diarrhea.
lymphocytes to migrate to and enter lymphoid tissue
(2) Shiga toxin (also known as verotoxin and Shiga-like patients with pertussis. The toxin inhibits signal transduc-
(spleen, lymph nodes). Because they do not enter tissue,
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Endotoxins mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
toxin) is an exotoxin produced primarily by strains of E. coli
there is an increase in their number in the blood (see the
with the O157:H7 serotype. These enterohemorrhagic
discussion of chemokines in Chapter 58).
strains cause bloody diarrhea and are the cause of out-
breaks associated with eating undercooked meat, especially
hamburger in fast-food restaurants. The toxin is named for
a very similar toxin produced by Shigella dysenteriae. The
Endotoxins are integral parts of the cell walls of both gram-
negative rods and cocci, in contrast to exotoxins, which are
toxin inactivates protein synthesis by removing adenine
from a specific site on the 28S rRNA in the large subunit of
actively released from the cell (see Table 7–9). In addition,
several other features distinguish these substances. Endo-
the human ribosome. The term verotoxin refers to its cyto-
pathic effect on Vero (monkey) cells in culture.
polypeptides; the enzymes that produce the LPS are
Shiga toxin is encoded by a temperate (lysogenic) bacte-
encoded by genes on the bacterial chromosome, rather
riophage. When Shiga toxin enters the bloodstream, it can
cause hemolytic–uremic syndrome (HUS). Shiga toxin toxins are lipopolysaccharides (LPS), whereas exotoxins are
than by plasmid or bacteriophage DNA, which usually
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com the endotoxins of some organisms are more effective than mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
binds to receptors on the kidney and on the endothelium of
encodes the exotoxins. The toxicity of endotoxins is low in
comparison with that of exotoxins. All endotoxins produce
small blood vessels. Inhibition of protein synthesis results
the same generalized effects of fever and shock, although
in death of those cells, leading to renal failure and microan-
giopathic hemolytic anemia. Certain antibiotics, such as
those of others (Figure 7–4). Endotoxins are weakly anti-
ciprofloxacin, can increase the amounts of Shiga toxin
genic; they induce protective antibodies so poorly that
produced by E. coli O157, which predisposes to HUS.
(3) The enterotoxins produced by V. cholerae, the agent
multiple episodes of toxicity can occur. No toxoids have
of cholera (see Chapter 18), and Bacillus cereus, a cause of
been produced from endotoxins, and endotoxins are not
diarrhea, act in a manner similar to that of the heat-labile
used as antigens in any available vaccine.
toxin of E. coli (Figure 7–3).
A major site of action of endotoxin is the macrophage.
(4) Pertussis toxin, produced by B. pertussis, the cause
negative bacteria in small pieces of outer membrane that bind
of whooping cough, is an exotoxin that catalyzes the trans-
fer of ADP-ribose from NAD to an inhibitory G protein. Endotoxins (LPS) are released from the surface of gram-
to LPS-binding protein in the plasma. This complex binds to
mebooksfree.com
a receptor on the surface of macrophages called CD14, which
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com cytokines such as interleukin-1 (IL-1), tumor necrosis factor mebooksfree.com
Inactivation of this inhibitory regulator has two effects:
one is in the stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity and a
activates toll-like receptor-4 (TLR-4). A signal cascade within
consequent increase in the amount of cyclic AMP within
the macrophage is then activated, resulting in the synthesis of
the affected cells (see Table 7–12). This results in edema
and other changes in the respiratory tract, leading to the
(TNF), and nitric oxide (see later and Figure 7-4).
The findings of fever and hypotension are salient fea-
cough of whooping cough. The second effect is the inhibi-
tures of septic shock. Additional features include
tion of the signal transduction pathway used by chemokine
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com