Page 262 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 262
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch09_229-250.indd Page 239 9/3/10 10:07 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch09_229-250.indd Page 239 9/3/10 10:07 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
IA IIA IIIB IVB VB VIB VIIB VIIIB IB IIB IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) (13) (14) (15) (16) (17)
4.0
3.5
3.0
F
2.5 4.0
O
Electro- 2.0 3.5
negativity H N
2.1 C 3.0
1.5
1.0 2.5
B Cl
0.5
Be 2.0 S 3.0
0
Li 1.5 P 2.5
1.0 Al Si 2.1 Br
Mg 1.8 Se 2.8
Na 1.2 Fe Co Ni Cu 1.5 As 2.4
0.9 Ti V Cr Mn 1.8 1.8 1.8 1.9 Zn Ga Ge 2.0
Sc 1.6 1.6 1.5 1.6 1.6 1.8 I
K Ca 1.3 1.5 Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te 2.5
1.9
0.8 1.0 Zr Nb 1.9 2.2 2.2 2.2 1.8 1.9 2.1
Sr Y 1.4 1.6 1.8 Os Ir Pt Au 1.7 1.7 At
Rb 1.2 Re 2.4 Hg Pb Bi Po
Tl
0.8 1.0 Hf Ta W 1.9 2.2 2.2 2.2 1.9 1.8 1.9 1.9 2.0 2.2
Ba La 1.5 1.7
Cs 1.3
0.7 0.9 1.1
Ra Ac
Fr 1.1
0.7 0.9
Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu
1.1
1.1 1.1 1.2 1.2 1.1 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.3
Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No
1.3 1.5 1.7 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.5
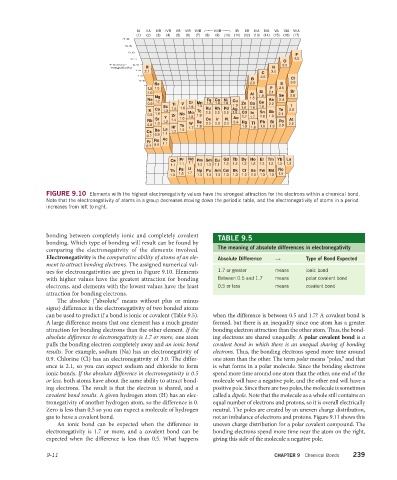
FIGURE 9.10 Elements with the highest electronegativity values have the strongest attraction for the electrons within a chemical bond.
Note that the electronegativity of atoms in a group decreases moving down the periodic table, and the electronegativity of atoms in a period
increases from left to right.
bonding between completely ionic and completely covalent TABLE 9.5
bonding. Which type of bonding will result can be found by
The meaning of absolute differences in electronegativity
comparing the electronegativity of the elements involved.
Electronegativity is the comparative ability of atoms of an ele- Absolute Difference → Type of Bond Expected
ment to attract bonding electrons. The assigned numerical val-
ues for electro negativities are given in Figure 9.10. Elements 1.7 or greater means ionic bond
with higher values have the greatest attraction for bonding Between 0.5 and 1.7 means polar covalent bond
electrons, and elements with the lowest values have the least 0.5 or less means covalent bond
attraction for bonding electrons.
The absolute (“absolute” means without plus or minus
signs) difference in the electronegativity of two bonded atoms
can be used to predict if a bond is ionic or covalent (Table 9.5). when the difference is between 0.5 and 1.7? A covalent bond is
A large difference means that one element has a much greater formed, but there is an inequality since one atom has a greater
attraction for bonding electrons than the other element. If the bonding electron attraction than the other atom. Thus, the bond-
absolute difference in electronegativity is 1.7 or more, one atom ing electrons are shared unequally. A polar covalent bond is a
pulls the bonding electron completely away and an ionic bond covalent bond in which there is an unequal sharing of bonding
results. For example, sodium (Na) has an electronegativity of electrons. Thus, the bonding electrons spend more time around
0.9. Chlorine (Cl) has an electronegativity of 3.0. The differ- one atom than the other. The term polar means “poles,” and that
ence is 2.1, so you can expect sodium and chloride to form is what forms in a polar molecule. Since the bonding electrons
ionic bonds. If the absolute difference in electronegativity is 0.5 spend more time around one atom than the other, one end of the
or less, both atoms have about the same ability to attract bond- molecule will have a negative pole, and the other end will have a
ing electrons. The result is that the electron is shared, and a positive pole. Since there are two poles, the molecule is sometimes
covalent bond results. A given hydrogen atom (H) has an elec- called a dipole. Note that the molecule as a whole still contains an
tronegativity of another hydrogen atom, so the difference is 0. equal number of electrons and protons, so it is overall electrically
Zero is less than 0.5 so you can expect a molecule of hydrogen neutral. The poles are created by an uneven charge distribution,
gas to have a covalent bond. not an imbalance of electrons and protons. Figure 9.11 shows this
An ionic bond can be expected when the difference in uneven charge distribution for a polar covalent compound. The
electronegativity is 1.7 or more, and a covalent bond can be bonding electrons spend more time near the atom on the right,
expected when the difference is less than 0.5. What happens giving this side of the molecule a negative pole.
9-11 CHAPTER 9 Chemical Bonds 239