Page 314 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 314
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch11_275-298.indd Page 291 9/3/10 6:12 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch11_275-298.indd Page 291 9/3/10 6:12 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
The key to “softening” hard water is to remove the trouble-
TABLE 11.6
some calcium and magnesium ions. If the hardness is caused by
Some common salts and their uses magnesium or calcium bicarbonates, the removal is accomplished
by simply heating the water. Upon heating, they decompose,
Common Name Formula Use
forming an insoluble compound that effectively removes the ions
Alum KAI(SO 4 ) 2 Medicine, canning, baking from solution. The decomposition reaction for calcium bicarbon-
powder
ate is
Baking soda NaHCO 3 Fire extinguisher, antacid, 2+
deodorizer, baking Ca (HCO 3 ) 2 (aq) → CaCO 3 (s) + H 2 O(l) + CO 2 ↑
powder
The reaction is the same for magnesium bicarbonate. As the
Bleaching powder CaOCl 2 Bleaching, deodorizer,
(chlorine tablets) disinfectant in solubility chart in appendix B shows, magnesium and calcium car-
swimming pools bonates are insoluble, so the ions are removed from solution in the
Borax Na 2 B 4 O 7 Water softener solid that is formed. Perhaps you have noticed such a white com-
pound forming around faucets if you live where bicarbonates are
Chalk CaCO 3 Antacid tablets, scouring
powder a problem. Commercial products to remove such deposits usually
Cobalt chloride CoCl 2 Hygrometer (pink in contain an acid, which reacts with the carbonate to make a new,
damp weather, blue in soluble salt that can be washed away.
dry weather) Water hardness is also caused by magnesium or calcium
Chile saltpeter NaNO 3 Fertilizer sulfate, which requires a different removal method. Certain
Epsom salt MgSO 4 ⋅7 H 2 O Laxative chemicals such as sodium carbonate (washing soda), trisodium
Fluorspar CaF 2 Metallurgy flux phosphate (TSP), and borax will react with the troublesome ions,
Gypsum CaSO 4 ⋅2 H 2 O Plaster of Paris, soil forming an insoluble solid that removes them from solution. For
conditioner example, washing soda and calcium sulfate react as follows:
Lunar caustic AgNO 3 Germicide and cauterizing Na 2 CO 3 (aq) + CaSO 4 (aq) → Na 2 SO 4 (aq) + CaCO 3 ↓
agent
Niter (or saltpeter) KNO 3 Meat preservative, makes Calcium carbonate is insoluble; thus, the calcium ions are re-
black gunpowder moved from solution before they can react with the soap. Many
(75 parts KNO 3 , 15 laundry detergents have Na 2 CO 3 , TSP, or borax (Na 2 B 4 O 7 )
of carbon, 10 of sulfur)
added to soften the water. TSP causes problems, however,
Potash K 2 CO 3 Makes soap, glass
because the additional phosphates in the wastewater can act as a
Rochelle salt KNaC 4 H 4 O 6 Baking powder ingredient fertilizer, stimulating the growth of algae to such an extent that
TSP Na 3 PO 4 Water softener, fertilizer other organisms in the water die.
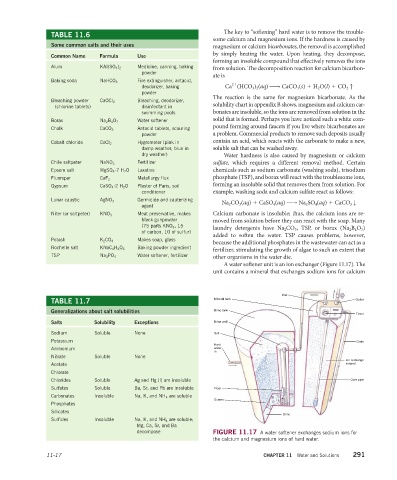
A water softener unit is an ion exchanger (Figure 11.17). The
unit contains a mineral that exchanges sodium ions for calcium
Inlet
TABLE 11.7 Mineral tank Outlet
Generalizations about salt solubilities Brine tank
Timer
Salts Solubility Exceptions Brine well
Sodium Soluble None Salt
Potassium Drain
Hard
Ammonium water
in
Nitrate Soluble None
Ion exchange
Acetate mineral
Chlorate
Chlorides Soluble Ag and Hg (l) are insoluble Core pipe
Sulfates Soluble Ba, Sr, and Pb are insoluble Float
Carbonates Insoluble Na, K, and NH 4 are soluble
Screen
Phosphates
Silicates
Brine
Sulfides Insoluble Na, K, and NH 4 are soluble;
Mg, Ca, Sr, and Ba
decompose FIGURE 11.17 A water softener exchanges sodium ions for
the calcium and magnesium ions of hard water.
11-17 CHAPTER 11 Water and Solutions 291