Page 357 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 357
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch13_323-350.indd Page 334 9/3/10 6:14 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch13_323-350.indd Page 334 9/3/10 6:14 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
the source and what shielding materials are between a person
and a source. A millirem is the unit of choice when low levels of
radiation are discussed.
Biological damage of damaging Biological damage
RADIATION EXPOSURE Threshold
Natural radioactivity is a part of your environment, and you dose
receive between 100 and 500 millirems each year from nat-
ural sources. This radiation from natural sources is called
background radiation. Background radiation comes from
outer space in the form of cosmic rays and from unstable
isotopes in the ground, building materials, and foods. Many 0 Increasing radiation exposure 0 Increasing radiation exposure
activities and situations will increase your yearly exposure to A B
radiation. For example, the atmosphere absorbs some of the
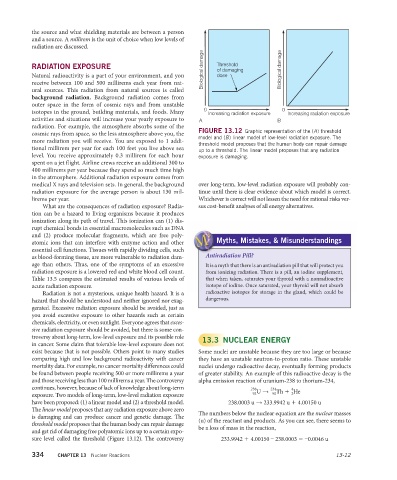
FIGURE 13.12 Graphic representation of the (A) threshold
cosmic rays from space, so the less atmosphere above you, the
model and (B) linear model of low-level radiation exposure. The
more radiation you will receive. You are exposed to 1 addi-
threshold model proposes that the human body can repair damage
tional millirem per year for each 100 feet you live above sea up to a threshold. The linear model proposes that any radiation
level. You receive approximately 0.3 millirem for each hour exposure is damaging.
spent on a jet flight. Airline crews receive an additional 300 to
400 millirems per year because they spend so much time high
in the atmosphere. Additional radiation exposure comes from
medical X rays and television sets. In general, the background over long-term, low-level radiation exposure will probably con-
radiation exposure for the average person is about 130 mil- tinue until there is clear evidence about which model is correct.
lirems per year. Whichever is correct will not lessen the need for rational risks ver-
What are the consequences of radiation exposure? Radia- sus cost-benefit analyses of all energy alternatives.
tion can be a hazard to living organisms because it produces
ionization along its path of travel. This ionization can (1) dis-
rupt chemical bonds in essential macromolecules such as DNA
and (2) produce molecular fragments, which are free poly-
atomic ions that can interfere with enzyme action and other Myths, Mistakes, & Misunderstandings
essential cell functions. Tissues with rapidly dividing cells, such
as blood-forming tissue, are more vulnerable to radiation dam- Antiradiation Pill?
age than others. Thus, one of the symptoms of an excessive It is a myth that there is an antiradiation pill that will protect you
radiation exposure is a lowered red and white blood cell count. from ionizing radiation. There is a pill, an iodine supplement,
Table 13.5 compares the estimated results of various levels of that when taken, saturates your thyroid with a nonradioactive
acute radiation exposure. isotope of iodine. Once saturated, your thyroid will not absorb
Radiation is not a mysterious, unique health hazard. It is a radioactive isotopes for storage in the gland, which could be
hazard that should be understood and neither ignored nor exag- dangerous.
gerated. Excessive radiation exposure should be avoided, just as
you avoid excessive exposure to other hazards such as certain
chemicals, electricity, or even sunlight. Everyone agrees that exces-
sive radiation exposure should be avoided, but there is some con-
troversy about long-term, low-level exposure and its possible role 13.3 NUCLEAR ENERGY
in cancer. Some claim that tolerable low-level exposure does not
exist because that is not possible. Others point to many studies Some nuclei are unstable because they are too large or because
comparing high and low background radioactivity with cancer they have an unstable neutron-to-proton ratio. These unstable
mortality data. For exam ple, no cancer mortality differences could nuclei undergo radioactive decay, eventually forming products
be found between people receiving 500 or more millirems a year of greater stability. An example of this radioactive decay is the
and those receiving less than 100 millirems a year. The controversy alpha emission reaction of uranium-238 to thorium-234,
continues, however, because of lack of knowledge about long-term 238 234 4
U → Th + He
92
90
2
exposure. Two models of long-term, low-level radiation exposure
have been proposed: (1) a linear model and (2) a threshold model. 238.0003 u → 233.9942 u + 4.00150 u
The linear model proposes that any radiation exposure above zero
The numbers below the nuclear equation are the nuclear masses
is damaging and can produce cancer and genetic damage. The
(u) of the reactant and products. As you can see, there seems to
threshold model proposes that the human body can repair damage
be a loss of mass in the reaction,
and get rid of damaging free polyatomic ions up to a certain expo-
sure level called the threshold (Figure 13.12). The controversy 233.9942 + 4.00150 – 238.0003 = –0.0046 u
334 CHAPTER 13 Nuclear Reactions 13-12