Page 359 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 359
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch13_323-350.indd Page 336 9/3/10 6:14 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch13_323-350.indd Page 336 9/3/10 6:14 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
A Closer Look
Nuclear Medicine
uclear medicine had its beginnings
N in 1946 when radioactive iodine was
first successfully used to treat thyroid can-
cer patients. Then physicians learned that
radioactive iodine could also be used as a
diagnostic tool, providing a way to measure
the function of the thyroid and to diagnose
thyroid disease. More and more physicians
began to use nuclear medicine to diagnose
thyroid disease as well as to treat hyper-
thyroidism and other thyroid problems.
Nuclear medicine is a branch of medicine
using radiation or radioactive materials to
diagnose as well as treat diseases.
The development of new nuclear medi-
cine technologies, such as cameras, detec-
tion instruments, and computers, has led to
a remarkable increase in the use of nuclear A B
medicine as a diagnostic tool. Today, there
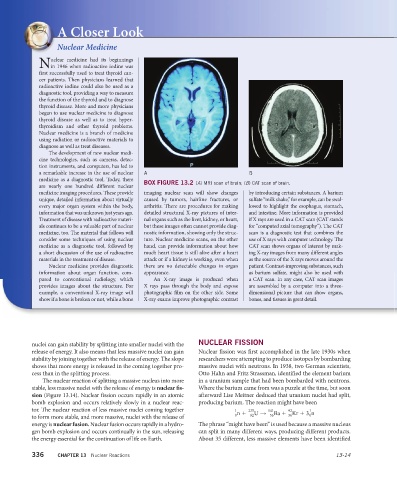
BOX FIGURE 13.2 (A) MRI scan of brain; (B) CAT scan of brain.
are nearly one hundred different nuclear
medicine imaging procedures. These provide imaging nuclear scan will show changes by introducing certain substances. A barium
unique, detailed information about virtually caused by tumors, hairline fractures, or sulfate “milk shake,” for example, can be swal-
every major organ system within the body, arthritis. There are procedures for making lowed to highlight the esophagus, stomach,
information that was unknown just years ago. detailed structural X-ray pictures of inter- and intestine. More information is provided
Treatment of disease with radioactive materi- nal organs such as the liver, kidney, or heart, if X rays are used in a CAT scan (CAT stands
als continues to be a valuable part of nuclear but these images often cannot provide diag- for “computed axial tomography”). The CAT
medicine, too. The material that follows will nostic information, showing only the struc- scan is a diagnostic test that combines the
consider some techniques of using nuclear ture. Nuclear medicine scans, on the other use of X rays with computer technology. The
medicine as a diagnostic tool, followed by hand, can provide information about how CAT scan shows organs of interest by mak-
a short discussion of the use of radioactive much heart tissue is still alive after a heart ing X-ray images from many different angles
materials in the treatment of disease. attack or if a kidney is working, even when as the source of the X rays moves around the
Nuclear medicine provides diagnostic there are no detectable changes in organ patient. Contrast-improving substances, such
information about organ function, com- appearance. as barium sulfate, might also be used with
pared to conventional radiology, which An X-ray image is produced when a CAT scan. In any case, CAT scan images
provides images about the structure. For X rays pass through the body and expose are assembled by a computer into a three-
example, a conventional X-ray image will photographic film on the other side. Some dimensional picture that can show organs,
show if a bone is broken or not, while a bone X-ray exams improve photographic contrast bones, and tissues in great detail.
nuclei can gain stability by splitting into smaller nuclei with the NUCLEAR FISSION
release of energy. It also means that less massive nuclei can gain Nuclear fission was first accomplished in the late 1930s when
stability by joining together with the release of energy. The slope researchers were attempting to produce isotopes by bombarding
shows that more energy is released in the coming together pro- massive nuclei with neutrons. In 1938, two German scientists,
cess than in the splitting process. Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassman, identified the element barium
The nuclear reaction of splitting a massive nucleus into more in a uranium sample that had been bombarded with neutrons.
stable, less massive nuclei with the release of energy is nuclear fi s- Where the barium came from was a puzzle at the time, but soon
sion (Figure 13.14). Nuclear fission occurs rapidly in an atomic afterward Lise Meitner deduced that uranium nuclei had split,
bomb explosion and occurs relatively slowly in a nuclear reac- producing barium. The reaction might have been
tor. The nuclear reaction of less massive nuclei coming together 1 235 141 92 1
n + U → Ba + Kr + 3 n
36
0
56
92
0
to form more stable, and more massive, nuclei with the release of
energy is nuclear fusion. Nuclear fusion occurs rapidly in a hydro- The phrase “might have been” is used because a massive nucleus
gen bomb explosion and occurs continually in the sun, releasing can split in many different ways, producing different products.
the energy essential for the continuation of life on Earth. About 35 different, less massive elements have been identified
336 CHAPTER 13 Nuclear Reactions 13-14