Page 506 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 506
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch19_477-500.indd Page 483 9/3/10 6:22 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch19_477-500.indd Page 483 9/3/10 6:22 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
Up
Down
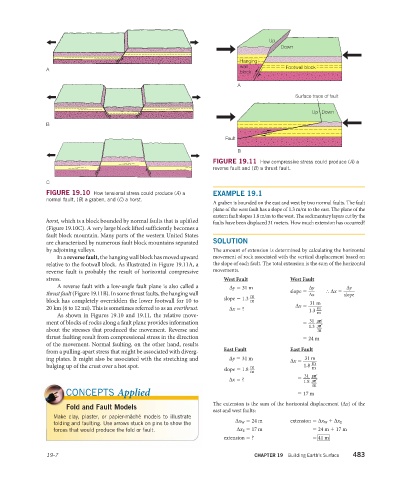
Hanging
wall Footwall block
A
block
A
Surface trace of fault
Up Down
B
Fault
B
FIGURE 19.11 How compressive stress could produce (A) a
reverse fault and (B) a thrust fault.
C
FIGURE 19.10 How tensional stress could produce (A) a EXAMPLE 19.1
normal fault, (B) a graben, and (C) a horst.
A graben is bounded on the east and west by two normal faults. The fault
plane of the west fault has a slope of 1.3 m/m to the east. The plane of the
eastern fault slopes 1.8 m/m to the west. The sedimentary layers cut by the
horst, which is a block bounded by normal faults that is uplifted faults have been displaced 31 meters. How much extension has occurred?
(Figure 19.10C). A very large block lifted sufficiently becomes a
fault block mountain. Many parts of the western United States
are characterized by numerous fault block mountains separated SOLUTION
by adjoining valleys. The amount of extension is determined by calculating the horizontal
In a reverse fault, the hanging wall block has moved upward movement of rock associated with the vertical displacement based on
relative to the footwall block. As illustrated in Figure 19.11A, a the slope of each fault. The total extension is the sum of the horizontal
reverse fault is probably the result of horizontal compressive movements.
stress. West Fault West Fault
A reverse fault with a low-angle fault plane is also called a Δy = 31 m _ _
Δy
Δy
thrust fault (Figure 19.11B). In some thrust faults, the hanging wall m _ slope = ∴ Δx = slope
Δx
block has completely overridden the lower footwall for 10 to slope = 1.3 m _
31 m
20 km (6 to 12 mi). This is sometimes referred to as an overthrust. Δx = ? Δx = 1.3
m _
As shown in Figures 19.10 and 19.11, the relative move- m
31 _ m _
ment of blocks of rocks along a fault plane provides information =
1.3 m _
about the stresses that produced the movement. Reverse and
m
thrust faulting result from compressional stress in the direction = 24 m
of the movement. Normal faulting, on the other hand, results
from a pulling-apart stress that might be associated with diverg- East Fault East Fault
31 m
ing plates. It might also be associated with the stretching and Δy = 31 m Δx = _
m _
bulging up of the crust over a hot spot. m _ 1.8
m
slope = 1.8
m
31 _ m _
Δx = ? =
1.8 m _
m
CONCEPTS Applied = 17 m
The extension is the sum of the horizontal displacement (Δx) of the
Fold and Fault Models
east and west faults:
Make clay, plaster, or papier-mâché models to illustrate
Δx W = 24 m
folding and faulting. Use arrows stuck on pins to show the extension = Δx W + Δx E
forces that would produce the fold or fault. Δx E = 17 m = 24 m + 17 m
extension = ? = 41 m
19-7 CHAPTER 19 Building Earth’s Surface 483