Page 509 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 509
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch19_477-500.indd Page 486 9/3/10 6:22 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch19_477-500.indd Page 486 9/3/10 6:22 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
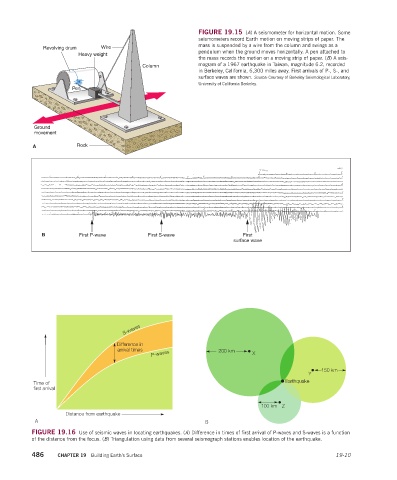
FIGURE 19.15 (A) A seismometer for horizontal motion. Some
seismometers record Earth motion on moving strips of paper. The
mass is suspended by a wire from the column and swings as a
Revolving drum Wire
pendulum when the ground moves horizontally. A pen attached to
Heavy weight
the mass records the motion on a moving strip of paper. (B) A seis-
Column mogram of a 1967 earthquake in Taiwan, magnitude 6.2, recorded
in Berkeley, California, 6,300 miles away. First arrivals of P-, S-, and
surface waves are shown. Source: Courtesy of Berkeley Seismological Laboratory,
University of California Berkeley.
Pen
Ground
movement
A Rock
B First P-wave First S-wave First
surface wave
S-waves
Difference in
arrival times 200 km
P-waves X
150 km
Y
Time of Earthquake
first arrival
100 km Z
Distance from earthquake
A B
FIGURE 19.16 Use of seismic waves in locating earthquakes. (A) Difference in times of first arrival of P-waves and S-waves is a function
of the distance from the focus. (B) Triangulation using data from several seismograph stations enables location of the earthquake.
486 CHAPTER 19 Building Earth’s Surface 19-10