Page 530 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 530
/Users/user-f465/Desktop
tiL12214_ch20_501-520.indd Page 507 9/3/10 6:23 PM user-f465
tiL12214_ch20_501-520.indd Page 507 9/3/10 6:23 PM user-f465 /Users/user-f465/Desktop
to a lower elevation by gravity acting through some intermedi-
ate agent, such as running water, wind, or glaciers. The erosion
of weathered materials as a result of gravity alone will be con-
sidered first.
MASS MOVEMENT
Gravity constantly acts on every mass of materials on the surface
of Earth, pulling parts of elevated regions toward lower levels.
Rocks in the elevated regions are able to temporarily resist this
constant pull through their cohesiveness with a main rock mass
or by the friction of the rock on a slope. Whenever anything hap-
pens to reduce the cohesiveness or to reduce the friction, gravity
pulls the freed material to a lower elevation. Thus, gravity acts Solid rock
directly on individual rock fragments and on large amounts of
Soil
surface materials as a mass, pulling all to a lower elevation. Ero-
sion caused by gravity acting directly is called mass movement
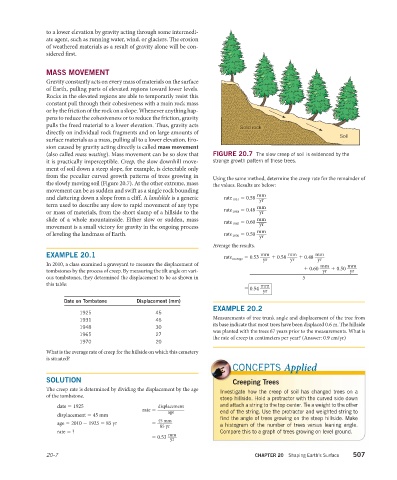
(also called mass wasting). Mass movement can be so slow that FIGURE 20.7 The slow creep of soil is evidenced by the
it is practically imperceptible. Creep, the slow downhill move- strange growth pattern of these trees.
ment of soil down a steep slope, for example, is detectable only
from the peculiar curved growth patterns of trees growing in Using the same method, determine the creep rate for the remainder of
the slowly moving soil (Figure 20.7). At the other extreme, mass the values. Results are below:
movement can be as sudden and swift as a single rock bounding
mm
and clattering down a slope from a cliff. A landslide is a generic rate 1931 = 0.58 _
yr
term used to describe any slow to rapid movement of any type _
mm
rate 1948 = 0.48
or mass of materials, from the short slump of a hillside to the yr
slide of a whole mountainside. Either slow or sudden, mass rate 1965 = 0.60 _
mm
movement is a small victory for gravity in the ongoing process yr
mm
of leveling the landmass of Earth. rate 1970 = 0.50 _
yr
Average the results.
mm
mm
EXAMPLE 20.1 rate average = 0.53 _ + 0.58 _ + 0.48 _
mm
yr yr yr
In 2010, a class examined a graveyard to measure the displacement of _ _
mm
mm
+ 0.60 + 0.50
tombstones by the process of creep. By measuring the tilt angle on vari- yr yr
ous tombstones, they determined the displacement to be as shown in 5
this table: _
mm
= 0.54
yr
Date on Tombstone Displacement (mm)
EXAMPLE 20.2
1925 45
Measurements of tree trunk angle and displacement of the tree from
1931 46
its base indicate that most trees have been displaced 0.6 m. The hillside
1948 30
was planted with the trees 67 years prior to the measurements. What is
1965 27
the rate of creep in centimeters per year? (Answer: 0.9 cm/yr)
1970 20
What is the average rate of creep for the hillside on which this cemetery
is situated?
CONCEPTS Applied
SOLUTION Creeping Trees
The creep rate is determined by dividing the displacement by the age
Investigate how the creep of soil has changed trees on a
of the tombstone.
steep hillside. Hold a protractor with the curved side down
date = 1925 _ and attach a string to the top center. Tie a weight to the other
displacement
rate = age end of the string. Use the protractor and weighted string to
displacement = 45 mm
_ find the angle of trees growing on the steep hillside. Make
45 mm
age = 2010 − 1925 = 85 yr =
85 yr a histogram of the number of trees versus leaning angle.
rate = ? Compare this to a graph of trees growing on level ground.
mm
= 0.53 _
yr
20-7 CHAPTER 20 Shaping Earth’s Surface 507