Page 43 - ACE YR IGCSE A TOP APPROACH TO CHEM
P. 43
C + O ➞ CO 2 Hydrogen gas:
2
Oxygen is reduced. Carbon is oxidised. Cracking of ethane [1]
(ii) Zinc oxide / ZnO [1] Cracking: Ethane ➞ ethene + hydrogen
An oxidising agent is a substance that will or
oxidise another substance and itself being
reduced. Reacting methane with steam [1]
2+
Zn + 2e ➞ Zn Methane + water ➞ carbon dioxide + hydrogen
(d) Carbon is less reactive than aluminium. [1] (b) Nitrogen and hydrogen are mixed under
200 atmospheres [1]
8 (a) The forward and backward reactions are at the Iron catalyst is used [1]
same rate. [1] at 450°C [1]
The concentrations of the reactants and Gases are compressed in a compressor at a pressure
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
products remain unchanged. [1] of 200 atmospheres.
(b) (i) Increases [1] The compressed gases then flow to a bed of hot iron
catalyst at 450°C.
2 [1]
The number of molecules of the reactants (c) To increase the rate of reaction [1]
is more than the number of molecules of (d) Lowering the temperature favours the
the products. [1] exothermic reaction. [1]
Higher pressure favours the side of equilibrium The equilibrium shifts to the right. [1]
with few gas molecules.
The equilibrium will shift to the right, and the (e) The equilibrium shifts to the right. [1]
yield increases. The yield increases. [1]
(ii) Remains the same [1] High pressure favours the side which produces
3 [1] fewer gas molecules. [1]
The number of molecules of the reactants The number of molecules for reactants is 4 and the
and the number of molecules of the number of molecules for product is 2.
products is the same. [1] (f) Low rate of reaction [1]
Increasing the pressure will not give effect
to an equilibrium when the reactants and 11 (a) Fossil fuel / sulfur bed [1]
products have the same number of molecules. (b) Increase the surface area [1]
(iii) Decreases [1] Increase the rate of reaction [1]
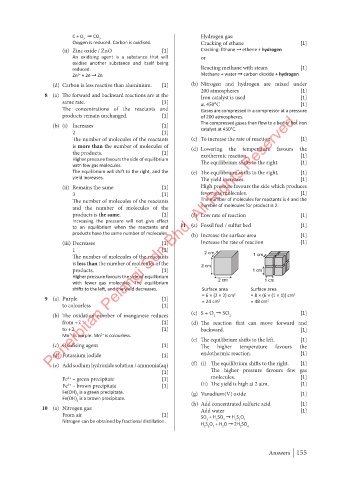
1 [1] 2 cm
The number of molecules of the reactants 1 cm
is less than the number of molecules of the 2 cm
products. [1] 1 cm
Higher pressure favours the side of equilibrium
with fewer gas molecules. The equilibrium 2 cm 1 cm
shifts to the left, and the yield decreases. Surface area Surface area
= 6 × (2 × 2) cm 2 = 8 × (6 × (1 × 1)) cm 2
9 (a) Purple [1] = 24 cm 2 = 48 cm 2
to colourless [1]
(b) The oxidation number of manganese reduces (c) S + O ➞ SO [1]
2
2
from +7 [1] (d) The reaction that can move forward and
to +2 [1] backward. [1]
Mn is purple. Mn is colourless.
2+
7+
(e) The equilibrium shifts to the left. [1]
(c) Oxidising agent [1] The higher temperature favours the
(d) Potassium iodide [1] endothermic reaction. [1]
(e) Add sodium hydroxide solution / ammonia(aq) (f) (i) The equilibrium shifts to the right. [1]
[1] The higher pressure favours few gas
Fe – green precipitate [1] molecules. [1]
2+
Fe – brown precipitate [1] (ii) The yield is high at 2 atm. [1]
3+
Fe(OH) is a green precipitate. (g) Vanadium(V) oxide [1]
2
Fe(OH) is a brown precipitate.
3 (h) Add concentrated sulfuric acid [1]
10 (a) Nitrogen gas: Add water [1]
From air [1] SO + H SO ➞ H S O
Nitrogen can be obtained by fractional distillation. 3 2 4 2 2 7
H S O + H O ➞ 2H SO
2 2 7 2 2 4
Answers 155
Answers.indd 155 3/4/22 3:54 PM