Page 44 - ACE YR IGCSE A TOP APPROACH TO CHEM
P. 44
12 (a) Zn(s) + CuCl (aq) ➞ ZnCl (aq) + Cu(s) 5 A
2 2
Aluminium oxide is an amphoteric oxide. An amphoteric
oxide can act as both an alkali and an acid. Therefore, it
0 +2 –1 +2 –1 0 neutralises both the acid and base.
1 mark if all oxidation numbers of reactants are 6 B 2+ –
Lead ion (Pb ) and iodide ion (I ) are needed to form
correct. [1] lead iodide.
1 mark if all oxidation numbers of products are
correct. [1] 7 C
Sulfur dioxide is acidic. It cannot neutralise acids.
(b) Yes [1] Zinc oxide is an amphoteric oxide. It neutralises both
The oxidation number of Zn changes from 0 to acids and bases.
+2. [1] Iron(III) oxide is alkaline. It neutralises acids.
It is an oxidation as the oxidation number Carbon monoxide is a neutral oxide. It has pH 7.
increases. [1] 8 D
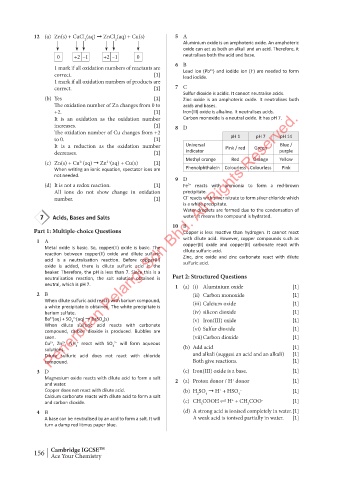
The oxidation number of Cu changes from +2 pH 1 pH 7 pH 14
to 0. [1]
It is a reduction as the oxidation number Universal Pink / red Green Blue /
decreases. [1] indicator purple
Methyl orange Red Orange Yellow
(c) Zn(s) + Cu (aq) ➞ Zn (aq) + Cu(s) [1]
2+
2+
When writing an ionic equation, spectator ions are Phenolphthalein Colourless Colourless Pink
not needed.
9 D
(d) It is not a redox reaction. [1] Fe reacts with ammonia to form a red-brown
3+
All ions do not show change in oxidation precipitate.
–
number. [1] Cl reacts with silver nitrate to form silver chloride which
is a white precipitate.
Water droplets are formed due to the condensation of
7 Acids, Bases and Salts water. It means the compound is hydrated.
10 B
Part 1: Multiple-choice Questions Copper is less reactive than hydrogen. It cannot react
with dilute acid. However, copper compounds such as
1 A Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
Metal oxide is basic. So, copper(II) oxide is basic. The copper(II) oxide and copper(II) carbonate react with
reaction between copper(II) oxide and dilute sulfuric dilute sulfuric acid.
acid is a neutralisation reaction. Before copper(II) Zinc, zinc oxide and zinc carbonate react with dilute
oxide is added, there is dilute sulfuric acid in the sulfuric acid.
beaker. Therefore, the pH is less than 7. Since this is a
neutralisation reaction, the salt solution obtained is Part 2: Structured Questions
neutral, which is pH 7. 1 (a) (i) Aluminium oxide [1]
2 B (ii) Carbon monoxide [1]
When dilute sulfuric acid reacts with barium compound, (iii) Calcium oxide [1]
a white precipitate is obtained. The white precipitate is
barium sulfate. (iv) silicon dioxide [1]
Ba (aq) + SO (aq) ➞ BaSO (s) (v) Iron(III) oxide [1]
2+
2–
4
4
When dilute sulfuric acid reacts with carbonate
compound, carbon dioxide is produced. Bubbles are (vi) Sulfur dioxide [1]
seen. (vii) Carbon dioxide [1]
Cu , Zn , NH react with SO will form aqueous
2–
2+
+
2+
4
4
solutions. (b) Add acid [1]
Dilute sulfuric acid does not react with chloride and alkali (suggest an acid and an alkali) [1]
compound. Both give reactions. [1]
3 D (c) Iron(III) oxide is a base. [1]
Magnesium oxide reacts with dilute acid to form a salt 2 (a) Proton donor / H donor [1]
+
and water.
Copper does not react with dilute acid. (b) H SO ➞ H + HSO [1]
+
–
Calcium carbonate reacts with dilute acid to form a salt 2 4 4
–
+
and carbon dioxide. (c) CH COOH L H + CH COO [1]
3
3
4 B (d) A strong acid is ionised completely in water. [1]
A base can be neutralised by an acid to form a salt. It will A weak acid is ionised partially in water. [1]
turn a damp red litmus paper blue.
Cambridge IGCSE TM
156 Ace Your Chemistry
Answers.indd 156 3/4/22 3:54 PM