Page 92 - Class-11-Physics-Part-1_Neat
P. 92
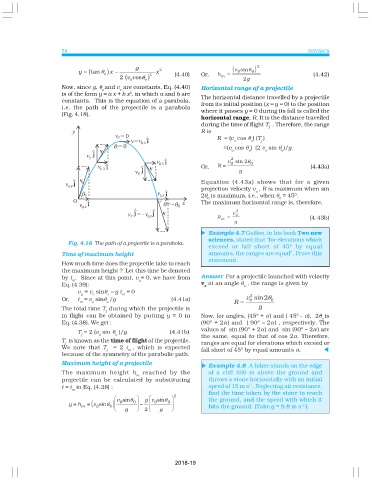
78 PHYSICS
g (v sinθ ) 2
y = (tan θ o ) x − 2 x 2 (4.40) Or, h = 0 0 (4.42)
2 v cosθ o ) m 2g
( o
Now, since g, θ and v are constants, Eq. (4.40) Horizontal range of a projectile
o o
2
is of the form y = a x + b x , in which a and b are
The horizontal distance travelled by a projectile
constants. This is the equation of a parabola,
from its initial position (x = y = 0) to the position
i.e. the path of the projectile is a parabola
where it passes y = 0 during its fall is called the
(Fig. 4.18).
horizontal range, R. It is the distance travelled
during the time of flight T . Therefore, the range
f
R is
R = (v cos θ ) (T )
o o f
=(v cos θ ) (2 v sin θ )/g
o o o o
2
v sin 2θ 0
0
Or, R = (4.43a)
g
Equation (4.43a) shows that for a given
projection velocity v , R is maximum when sin
o
2θ is maximum, i.e., when θ = 45 .
0
0 0
The maximum horizontal range is, therefore,
2
v 0
R = (4.43b)
m
g
Example 4.7 Galileo, in his book Two new
t
sciences, stated that “for elevations which
Fig. 4.18 The path of a projectile is a parabola.
exceed or fall short of 45° by equal
Time of maximum height amounts, the ranges are equal”. Prove this
statement.
How much time does the projectile take to reach
the maximum height ? Let this time be denoted
by t . Since at this point, v = 0, we have from Answer For a projectile launched with velocity
m y
Eq. (4.39): v at an angle θ , the range is given by
o
o
v = v sinθ – g t = 0
y o o m 2
Or, t = v sinθ /g (4.41a) v 0 sin2θ 0
m o o R =
The total time T during which the projectile is g
f
in flight can be obtained by putting y = 0 in Now, for angles, (45° + α) and ( 45° – α), 2θ is
o
Eq. (4.38). We get : (90° + 2α) and ( 90° – 2α) , respectively. The
values of sin (90° + 2α) and sin (90° – 2α) are
T = 2 (v sin θ )/g (4.41b)
f o o the same, equal to that of cos 2α. Therefore,
T is known as the time of flight of the projectile.
f ranges are equal for elevations which exceed or
We note that T = 2 t , which is expected
f m fall short of 45° by equal amounts α. t
because of the symmetry of the parabolic path.
Maximum height of a projectile
Example 4.8 A hiker stands on the edge
t
The maximum height h reached by the of a cliff 490 m above the ground and
m
projectile can be calculated by substituting throws a stone horizontally with an initial
-1
t = t in Eq. (4.38) : speed of 15 m s . Neglecting air resistance,
m
find the time taken by the stone to reach
2
0
0
y = h = (v sinθ ) v sinθ 0 − g v sinθ 0 the ground, and the speed with which it
-2
m 0 0 hits the ground. (Take g = 9.8 m s ).
g 2 g
2018-19