Page 24 - Drug Discovery and Development: Prospects and Challenges
P. 24
14 / Drug Discovery and Development: Prospects and Challenges
Brothers and sisters,
Ladies and Gentlemen,
Anti-cancer/Cytotoxicity
Various cytotoxic and anti-cancer studies have used 4,5-dimethylthiazol-
2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) and its improved MTS
assay. Firstly introduced by Mossman in 1983, the MTT assay uses
mitochondrial reductase enzymes produced by live cells to convert MTT
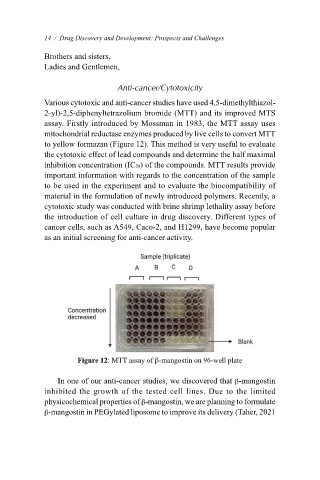
to yellow formazan (Figure 12). This method is very useful to evaluate
the cytotoxic effect of lead compounds and determine the half maximal
inhibition concentration (IC50) of the compounds. MTT results provide
important information with regards to the concentration of the sample
to be used in the experiment and to evaluate the biocompatibility of
material in the formulation of newly introduced polymers. Recently, a
cytotoxic study was conducted with brine shrimp lethality assay before
the introduction of cell culture in drug discovery. Different types of
cancer cells, such as A549, Caco-2, and H1299, have become popular
as an initial screening for anti-cancer activity.
Figure 12: MTT assay of b-mangostin on 96-well plate
In one of our anti-cancer studies, we discovered that b-mangostin
inhibited the growth of the tested cell lines. Due to the limited
physicochemical properties of b-mangostin, we are planning to formulate
b-mangostin in PEGylated liposome to improve its delivery (Taher, 2021