Page 121 - spectroscopic-atlas-5_0-english_Neat
P. 121
Spectroscopic Atlas for Amateur Astronomers 121
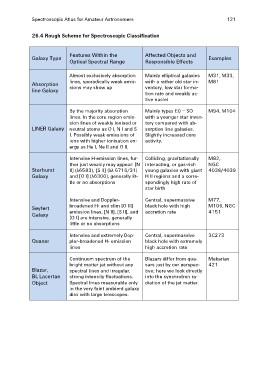
26.4 Rough Scheme for Spectroscopic Classification
Galaxy Type Features Within the Affected Objects and Examples
Optical Spectral Range Responsible Effects
Absorption Almost exclusively absorption Mainly elliptical galaxies M31, M33,
line Galaxy lines, sporadically weak emis- with a rather old star in- M81
sions may show up ventory, low star forma-
tion rate and weakly ac-
tive nuclei
By the majority absorption Mainly types E0 – SO M94, M104
lines. In the core region emis- with a younger star inven-
LINER Galaxy sion lines of weakly ionised or tory compared with ab-
neutral atoms as O I, N I and S sorption line galaxies.
I. Possibly weak emissions of Slightly increased core
ions with higher ionisation en- activity.
ergy as He I, Ne II and O II.
Starburst Intensive H-emission lines, fur- Colliding, gravitationally M82,
Galaxy ther just weakly may appear: [N interacting, or gas-rich NGC
II] (λ6583), [S II] (λλ 6716/31) young galaxies with giant 4038/4039
and [O I] (λ6300), generally lit- H II regions and a corre-
tle or no absorptions spondingly high rate of
star birth
Seyfert Intensive and Doppler- Central, supermassive M77,
Galaxy broadened H- and slim [O III] black hole with high M106, NGC
emission lines, [N II], [S II], and accretion rate 4151
[O I] are intensive, generally
little or no absorptions
Intensive and extremely Dop- Central, supermassive 3C273
pler-broadened H- emission
Quasar lines black hole with extremely
high accretion rate
Continuum spectrum of the Blazars differ from qua- Makarian
bright matter jet without any sars just by our perspec- 421
spectral lines and irregular, tive; here we look directly
Blazar, strong intensity fluctuations. into the synchrotron ra-
BL Lacertae Spectral lines measurable only diation of the jet matter.
Object in the very faint ambient galaxy
disk with large telescopes.