Page 308 - The Book of Caterpillars: A Life-Size Guide to Six Hundred Species From Around the World
P. 308
MOTH CATERPILLARS
FAMILY Limacodidae
DISTRIBUTION Eastern Siberia, Japan, Korea, eastern China, and Chinese Taipei
HABITAT Forests, agricultural land, parks, and gardens
HOST PLANTS Many, including willow (Salix spp.), poplar (Populus spp.),
chestnut (Castanea spp.), persimmon (Diospyros spp.),
Citrus spp., and many other fruit trees
NOTE Caterpillar that spends almost a year in the prepupal stage
CONSERVATION STATUS Not evaluated, but extremely common
ADULT WINGSPAN
1⅜–1 ⁄ in (35–40 mm)
CATERPILLAR LENGTH
1–1⅛ in (25–28 mm)
PARASA CONSOCIA
PARASA CONSOCIA
306
WALKER, 1865
Parasa consocia caterpillars hatch from up to 150 eggs laid
in small batches over a seven-day period. For the rst couple
of instars, the larvae are gregarious, grazing only the surface of
leaves. They then disperse for the remainder of the eight or nine
instars (totaling 27 to 37 days), devouring the entire leaf. Food
Actual size
consumption in the nal instar constitutes 80 percent of the total.
The caterpillars overwinter inside a dark brown, oval cocoon,
wedged into tree bark or in the soil, often in aggregations, for
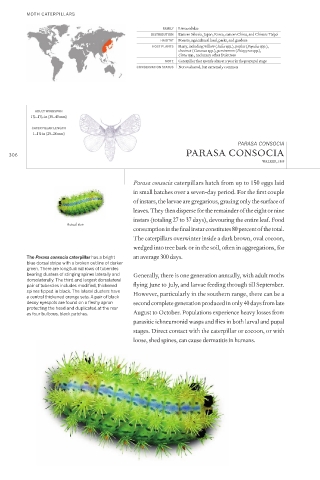
The Parasa consocia caterpillar has a bright an average 300 days.
blue dorsal stripe with a broken outline of darker
green. There are longitudinal rows of tubercles
bearing clusters of stinging spines laterally and Generally, there is one generation annually, with adult moths
dorsolaterally. The third and largest dorsolateral
pair of tubercles includes modi ed, thickened ying June to July, and larvae feeding through till September.
spines tipped in black. The lateral clusters have However, particularly in the southern range, there can be a
a central thickened orange seta. A pair of black
decoy eyespots are found on a eshy apron second complete generation produced in only 40 days from late
protecting the head and duplicated at the rear
as four bulbous, black patches. August to October. Populations experience heavy losses from
parasitic ichneumonid wasps and ies in both larval and pupal
stages. Direct contact with the caterpillar or cocoon, or with
loose, shed spines, can cause dermatitis in humans.