Page 318 - (DK) Ocean - The Definitive Visual Guide
P. 318
316 ANIMAL LIFE
PHYLUM TARDIGRADA
claw
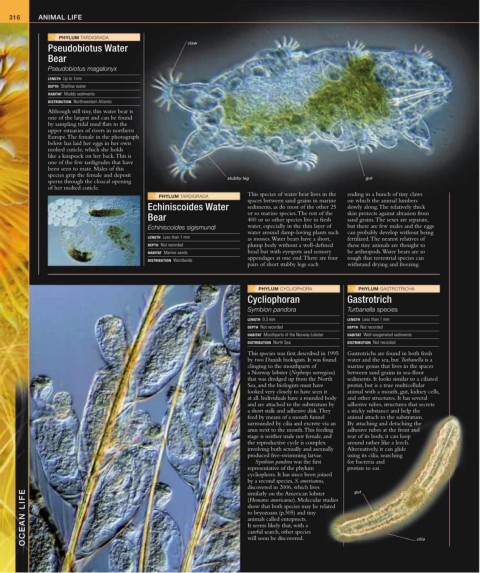
Pseudobiotus Water
Bear
Pseudobiotus magalonyx
LENGTH Up to 1mm
DEPTH Shallow water
HABITAT Muddy sediments
DISTRIBUTION Northwestern Atlantic
Although still tiny, this water bear is
one of the largest and can be found
by sampling tidal mud flats in the
upper estuaries of rivers in northern
Europe. The female in the photograph
below has laid her eggs in her own
molted cuticle, which she holds
like a knapsack on her back. This is
one of the few tardigrades that have
been seen to mate. Males of this
species grip the female and deposit gut
sperm through the cloacal opening stubby leg
of her molted cuticle.
PHYLUM TARDIGRADA This species of water bear lives in the ending in a bunch of tiny claws
spaces between sand grains in marine on which the animal lumbers
Echiniscoides Water sediments, as do most of the other 25 slowly along. The relatively thick
or so marine species. The rest of the skin protects against abrasion from
Bear 400 or so other species live in fresh sand grains. The sexes are separate,
water, especially in the thin layer of but there are few males and the eggs
Echiniscoides sigismundi
water around damp-loving plants such can probably develop without being
LENGTH Less than 1 mm as mosses. Water bears have a short, fertilized. The nearest relatives of
DEPTH Not recorded plump body without a well-defined these tiny animals are thought to
HABITAT Marine sands head but with eyespots and sensory be arthropods. Water bears are so
appendages at one end. There are four tough that terrestrial species can
DISTRIBUTION Worldwide
pairs of short stubby legs each withstand drying and freezing.
PHYLUM CYCLIOPHORA PHYLUM GASTROTRICHA
Cycliophoran Gastrotrich
Turbanella species
Symbion pandora
LENGTH 0.3 mm LENGTH Less than 1 mm
DEPTH Not recorded DEPTH Not recorded
HABITAT Mouthparts of the Norway Lobster HABITAT Well-oxygenated sediments
DISTRIBUTION North Sea DISTRIBUTION Not recorded
This species was first described in 1995 Gastrotrichs are found in both fresh
by two Danish biologists. It was found water and the sea, but Turbanella is a
clinging to the mouthparts of marine genus that lives in the spaces
a Norway lobster (Nephrops norvegicus) between sand grains in sea-floor
that was dredged up from the North sediments. It looks similar to a ciliated
Sea, and the biologists must have protist, but is a true multicellular
looked very closely to have seen it animal with a mouth, gut, kidney cells,
at all. Individuals have a rounded body and other structures. It has several
and are attached to the substratum by adhesive tubes, structures that secrete
a short stalk and adhesive disk. They a sticky substance and help the
feed by means of a mouth funnel animal attach to the substratum.
surrounded by cilia and excrete via an By attaching and detaching the
anus next to the mouth. This feeding adhesive tubes at the front and
stage is neither male nor female, and rear of its body, it can loop
the reproductive cycle is complex around rather like a leech.
involving both sexually and asexually Alternatively, it can glide
produced free-swimming larvae. using its cilia, searching
Symbion pandora was the first for bacteria and
representative of the phylum protists to eat.
cycliophora. It has since been joined
by a second species, S. americanus,
discovered in 2006, which lives gut
OCEAN LIFE show that both species may be related cilia
similarly on the American lobster
(Homarus americanus). Molecular studies
to bryozoans (p.305) and tiny
animals called entoprocts.
It seems likely that, with a
careful search, other species
will soon be discovered.