Page 317 - (DK) Ocean - The Definitive Visual Guide
P. 317
SMALL, BOTTOM-LIVING PHYLA 315
PHYLUM CEPHALORHYNCHA PHYLUM VESTIMENTIFERA pulling itself down with its pedicle.
Fossils of brachiopods with a similar
Mud Dragon Linguid Brachiopod shape appear in rocks that are
500 million years old.
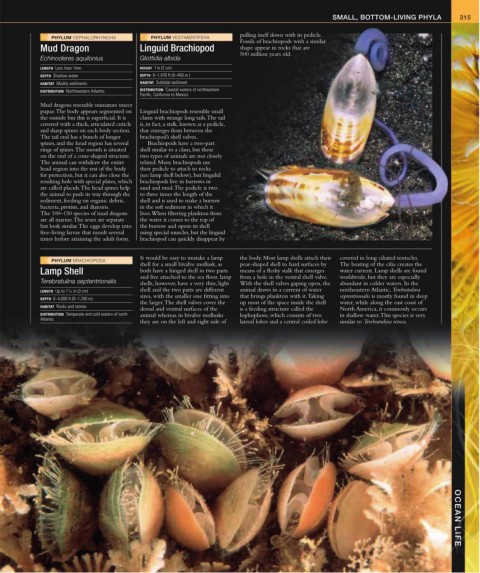
Echinoderes aquilonius Glottidia albida
LENGTH Less than 1mm HEIGHT 1 in (2 cm)
DEPTH Shallow water DEPTH 0–1,476 ft (0–450 m )
HABITAT Muddy sediments HABITAT Subtidal sediment
DISTRIBUTION Northwestern Atlantic DISTRIBUTION Coastal waters of northeastern
Pacific, California to Mexico
Mud dragons resemble miniature insect
pupae. The body appears segmented on Linguid brachiopods resemble small
the outside but this is superficial. It is clams with strange long tails. The tail
covered with a thick, articulated cuticle is, in fact, a stalk, known as a pedicle,
and sharp spines on each body section. that emerges from between the
The tail end has a bunch of longer brachiopod’s shell valves.
spines, and the head region has several Brachiopods have a two-part
rings of spines. The mouth is situated shell similar to a clam, but these
on the end of a cone-shaped structure. two types of animals are not closely
The animal can withdraw the entire related. Many brachiopods use
head region into the rest of the body their pedicle to attach to rocks
for protection, but it can also close the (see lamp shell below), but lingulid
resulting hole with special plates, which brachiopods live in burrows in
are called placids. The head spines help sand and mud. The pedicle is two
the animal to push its way through the to three times the length of the
sediment, feeding on organic debris, shell and is used to make a burrow
bacteria, protists, and diatoms. in the soft sediment in which it
The 100–150 species of mud dragons lives. When filtering plankton from
are all marine. The sexes are separate the water it comes to the top of
but look similar. The eggs develop into the burrow and opens its shell
free-living larvae that moult several using special muscles, but the linguid
times before attaining the adult form. brachiopod can quickly disappear by
It would be easy to mistake a lamp the body. Most lamp shells attach their covered in long ciliated tentacles.
PHYLUM BRACHIOPODA
shell for a small bivalve mollusk, as pear-shaped shell to hard surfaces by The beating of the cilia creates the
Lamp Shell both have a hinged shell in two parts means of a fleshy stalk that emerges water current. Lamp shells are found
and live attached to the sea floor. lamp from a hole in the ventral shell valve. worldwide, but they are especially
shells, however, have a very thin, light With the shell valves gaping open, the abundant in colder waters. In the
Terebratulina septentrionalis
1
LENGTH Up to 1 / 4 in (3 cm) shell and the two parts are different animal draws in a current of water northeastern Atlantic, Terebratulina
sizes, with the smaller one fitting into that brings plankton with it. Taking septentrionalis is mostly found in deep
DEPTH 0–4,000 ft (0–1,200 m)
the larger. The shell valves cover the up most of the space inside the shell water, while along the east coast of
HABITAT Rocks and stones
dorsal and ventral surfaces of the is a feeding structure called the North America, it commonly occurs
DISTRIBUTION Temperate and cold waters of north animal whereas in bivalve mollusks lophophore, which consists of two in shallow water. This species is very
Atlantic
they are on the left and right side of lateral lobes and a central coiled lobe similar to Terebratulina retusa. OCEAN LIFE