Page 319 - (DK) Ocean - The Definitive Visual Guide
P. 319
PLANKTONIC PHYLA 317
Planktonic Phyla
OF THE MANY MAJOR GROUPS (phyla) of invertebrate animals,
DOMAIN Eucarya
a few are entirely composed of planktonic animals. Like all
KINGDOM Animalia
animals, they are classified into different phyla based on
PHYLA Ctenophora
their anatomy, which can be complex. All are ecologically
Chaetognatha
important because the plankton community underpins all
Rotifera
the ocean food chains. Three minor phyla (Ctenophora,
SPECIES About 2,332
Chaetognatha and Rotifera)
are represented here.
Predators
Carnivorous zooplankton have many methods of catching prey.
Comb jellies are voracious predators—some trap their prey with
a sticky secretion released from special cells (colloblasts) lining
their tentacles. Others draw in prey using negative pressure
created by rapidly opening their mouths. Species of Haeckelia
HOOKING PREY
even recycle the stinging cells from their cnidarian prey. This arrow-worm has
Arrow-worms have vibration sensors to detect prey, which is brown-colored hooks on
caught and held by moveable hooks. The prey is then paralyzed either side of its circular
mouth for holding prey.
by neurotoxins released from pores adjacent to the mouth.
Grazers
Some of the zooplankton are herbivorous, grazing on
phytoplankton or filter feeding. Some planktonic rotifers GLEAMING
feed on organic particles suspended in the water. The cilia CILIA
on the crown that surrounds the oral cavity waft water Comb jellies,
or sea gooseberries,
into a food groove leading to the mouth. Here, food
ROTIFER FEEDING METHOD swim by beating
The rotifer’s ciliated crown, particles are sifted and returned to the pharynx where eight vertical rows of
used in locomotion and filter jawlike structures, called trophi, grind the food before it cilia combs, which shimmer
feeding, is visible on the left. passes into the stomach. Trophi are unique to rotifers. with iridescent colors.
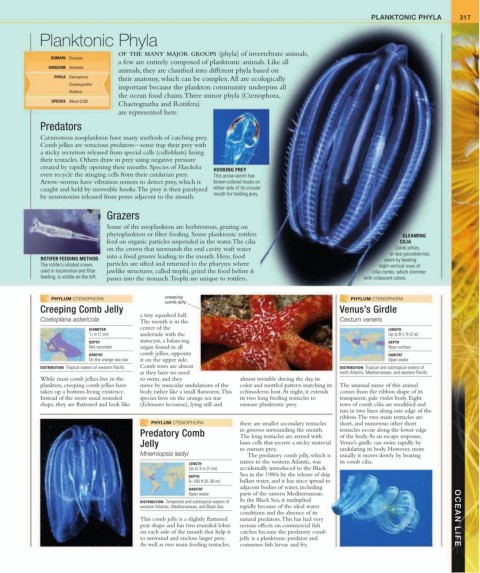
PHYLUM CTENOPHORA creeping PHYLUM CTENOPHORA
comb jelly
Creeping Comb Jelly Venus’s Girdle
a tiny squashed ball.
The mouth is in the
Coeloplana astericola Cestum veneris
DIAMETER center of the LENGTH
1 / 2 in (1 cm) underside with the Up to 6 / 2 ft (2 m)
1
DEPTH statocyst, a balancing DEPTH
Not recorded organ found in all Near surface
HABITAT comb jellies, opposite HABITAT
On the orange sea star it on the upper side. Open water
DISTRIBUTION Tropical waters of western Pacific Comb rows are absent DISTRIBUTION Tropical and subtropical waters of
as they have no need north Atlantic, Mediterranean, and western Pacific
While most comb jellies live in the to swim, and they almost invisible during the day, its
plankton, creeping comb jellies have move by muscular undulations of the color and mottled pattern matching its The unusual name of this animal
taken up a bottom-living existence. body rather like a small flatworm. This echinoderm host. At night, it extends comes from the ribbon shape of its
Instead of the more usual rounded species lives on the orange sea star its two long feeding tentacles to transparent, pale violet body. Eight
shape, they are flattened and look like (Echinaster luzonicus), lying still and ensnare planktonic prey. rows of comb cilia are modified and
run in two lines along one edge of the
ribbon. The two main tentacles are
PHYLUM CTENOPHORA there are smaller secondary tentacles short, and numerous other short
Predatory Comb in grooves surrounding the mouth. tentacles occur along the lower edge
The long tentacles are armed with
of the body. As an escape response,
Jelly lasso cells that secrete a sticky material Venus’s girdle can swim rapidly by
to ensnare prey. undulating its body. However, more
The predatory comb jelly, which is usually it moves slowly by beating
Mnemiopsis leidyi
native to the western Atlantic, was its comb cilia.
LENGTH
Up to 3 in (7 cm) accidentally introduced to the Black
Sea in the 1980s by the release of ship
DEPTH
0–100 ft (0–30 m) ballast water, and it has since spread to
adjacent bodies of water, including
HABITAT
Open water parts of the eastern Mediterranean.
In the Black Sea, it multiplied
DISTRIBUTION Temperate and subtropical waters of
western Atlantic, Mediterranean, and Black Sea rapidly because of the ideal water
conditions and the absence of its
This comb jelly is a slightly flattened natural predators. This has had very OCEAN LIFE
pear shape and has two rounded lobes serious effects on commercial fish
on each side of the mouth that help it catches because the predatory comb
to surround and enclose larger prey. jelly is a planktonic predator and
As well as two main feeding tentacles, consumes fish larvae and fry.