Page 322 - (DK) Ocean - The Definitive Visual Guide
P. 322
320 ANIMAL LIFE
Jawless Fishes
JAWLESS FISH FORM AN ANCIENT group of vertebrates
DOMAIN Eucarya
encompassing a diverse range of extinct groups. Today,
KINGDOM Animalia
there are only two small groups: the lampreys and the
PHYLUM Chordata
hagfish. They are considered to be the most primitive
CLASSES Myxini
living vertebrates, although many scientists do not
Cephalaspidomorphi
regard hagfish as true vertebrates. Hagfish and
SPECIES 125
lampreys look similar, with elongated bodies and
jawless mouths, but the two groups evolved along separate lines. Lampreys
live in temperate coastal waters throughout the world and swim up rivers to
breed, although some remain in fresh water. Hagfish are exclusively marine.
Anatomy
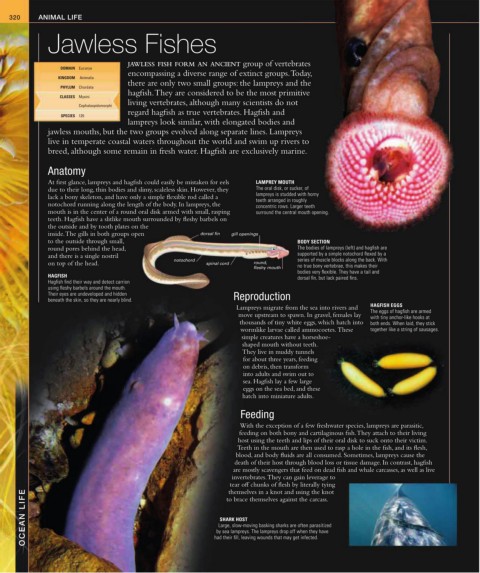
At first glance, lampreys and hagfish could easily be mistaken for eels LAMPREY MOUTH
due to their long, thin bodies and slimy, scaleless skin. However, they The oral disk, or sucker, of
lack a bony skeleton, and have only a simple flexible rod called a lampreys is studded with horny
teeth arranged in roughly
notochord running along the length of the body. In lampreys, the concentric rows. Larger teeth
mouth is in the center of a round oral disk armed with small, rasping surround the central mouth opening.
teeth. Hagfish have a slitlike mouth surrounded by fleshy barbels on
the outside and by tooth plates on the
inside. The gills in both groups open dorsal fin gill openings
to the outside through small, BODY SECTION
round pores behind the head, The bodies of lampreys (left) and hagfish are
and there is a single nostril supported by a simple notochord flexed by a
notochord series of muscle blocks along the back. With
on top of the head. spinal cord round, no true bony vertebrae, this makes their
fleshy mouth
bodies very flexible. They have a tail and
HAGFISH dorsal fin, but lack paired fins.
Hagfish find their way and detect carrion
using fleshy barbels around the mouth.
Their eyes are undeveloped and hidden Reproduction
beneath the skin, so they are nearly blind.
Lampreys migrate from the sea into rivers and HAGFISH EGGS
The eggs of hagfish are armed
move upstream to spawn. In gravel, females lay with tiny anchor-like hooks at
thousands of tiny white eggs, which hatch into both ends. When laid, they stick
wormlike larvae called ammocoetes. These together like a string of sausages.
simple creatures have a horseshoe-
shaped mouth without teeth.
They live in muddy tunnels
for about three years, feeding
on debris, then transform
into adults and swim out to
sea. Hagfish lay a few large
eggs on the sea bed, and these
hatch into miniature adults.
Feeding
With the exception of a few freshwater species, lampreys are parasitic,
feeding on both bony and cartilaginous fish. They attach to their living
host using the teeth and lips of their oral disk to suck onto their victim.
Teeth in the mouth are then used to rasp a hole in the fish, and its flesh,
blood, and body fluids are all consumed. Sometimes, lampreys cause the
death of their host through blood loss or tissue damage. In contrast, hagfish
are mostly scavengers that feed on dead fish and whale carcasses, as well as live
invertebrates. They can gain leverage to
tear off chunks of flesh by literally tying
OCEAN LIFE had their fill, leaving wounds that may get infected.
themselves in a knot and using the knot
to brace themselves against the carcass.
SHARK HOST
Large, slow-moving basking sharks are often parasitized
by sea lampreys. The lampreys drop off when they have