Page 390 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 390
346 SEcTion iii EndocrinE ` endocrine—PAthology EndocrinE ` endocrine—PAthology
Diabetes mellitus
AcUte mAniFestAtions Polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia, weight loss, DKA (type 1), hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state
(type 2).
Rarely, can be caused by unopposed secretion of GH and epinephrine. Also seen in patients on
glucocorticoid therapy (steroid diabetes).
chronic comPlicAtions Nonenzymatic glycation:
Small vessel disease (diffuse thickening of basement membrane) retinopathy (hemorrhage,
exudates, microaneurysms, vessel proliferation), glaucoma, nephropathy. Nodular
glomerulosclerosis progressive proteinuria (initially microalbuminuria; ACE inhibitors
and ARBs are renoprotective) and arteriolosclerosis (causing hypertension) chronic kidney
disease.
Large vessel atherosclerosis, CAD, peripheral vascular occlusive disease, gangrene limb loss,
cerebrovascular disease. MI most common cause of death.
Osmotic damage (sorbitol accumulation in organs with aldose reductase and or absent sorbitol
dehydrogenase):
Neuropathy (motor, sensory [glove and stocking distribution], and autonomic degeneration).
Cataracts.
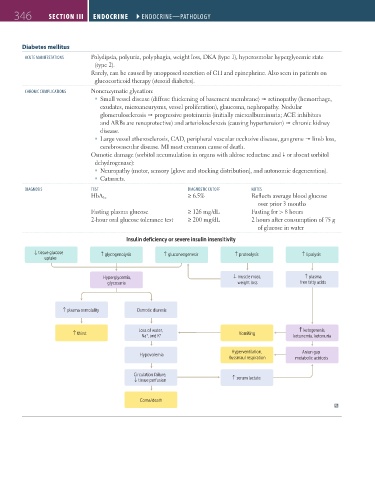
diAgnosis test diAgnostic cUtoFF notes
HbA 1c ≥ 6.5% Reflects average blood glucose
over prior 3 months
Fasting plasma glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL Fasting for > 8 hours
2-hour oral glucose tolerance test ≥ 200 mg/dL 2 hours after consumption of 75 g
of glucose in water
Insulin deficiency or severe insulin insensitivity
tissue glucose ↑ glycogenolysis ↑ gluconeogenesis ↑ proteolysis ↑ lipolysis
↑
uptake
Hyperglycemia, ↓ muscle mass, ↑ plasma
glycosuria weight loss free fatty acids
↑ plasma osmolality Osmotic diuresis
Loss of water, ↑ ketogenesis,
↑ thirst + + Vomiting
Na , and K ketonemia, ketonuria
Hyperventilation, Anion gap
Hypovolemia
Kussmaul respiration metabolic acidosis
Circulation failure,
↓ tissue perfusion ↑ serum lactate
Coma/death
FAS1_2019_08-Endocrine.indd 346 11/7/19 4:30 PM