Page 571 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 571
Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology SecTioN iii 527
Adult primary brain tumors (continued)
tumor desCriPtion histology
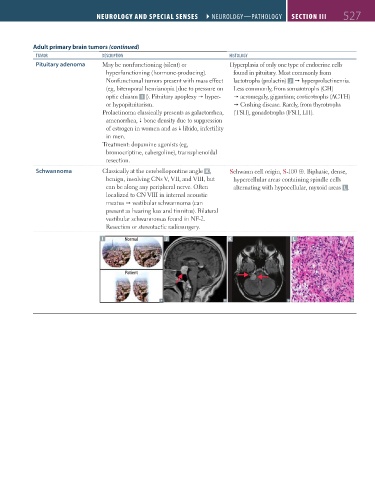
Pituitary adenoma May be nonfunctioning (silent) or Hyperplasia of only one type of endocrine cells
hyperfunctioning (hormone-producing). found in pituitary. Most commonly from
Nonfunctional tumors present with mass effect lactotrophs (prolactin) J hyperprolactinemia.
(eg, bitemporal hemianopia [due to pressure on Less commonly, from somatotrophs (GH)
optic chiasm I ]). Pituitary apoplexy hyper- acromegaly, gigantism; corticotrophs (ACTH)
or hypopituitarism. Cushing disease. Rarely, from thyrotrophs
Prolactinoma classically presents as galactorrhea, (TSH), gonadotrophs (FSH, LH).
amenorrhea, bone density due to suppression
of estrogen in women and as libido, infertility
in men.
Treatment: dopamine agonists (eg,
bromocriptine, cabergoline), transsphenoidal
resection.
Schwannoma Classically at the cerebellopontine angle K , Schwann cell origin, S-100 ⊕. Biphasic, dense,
benign, involving CNs V, VII, and VIII, but hypercellular areas containing spindle cells
can be along any peripheral nerve. Often alternating with hypocellular, myxoid areas L .
localized to CN VIII in internal acoustic
meatus vestibular schwannoma (can
present as hearing loss and tinnitus). Bilateral
vestibular schwannomas found in NF-2.
Resection or stereotactic radiosurgery.
I Normal J K L
Patient
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 527 11/8/19 7:39 AM