Page 572 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 572
528 SecTioN iii Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology
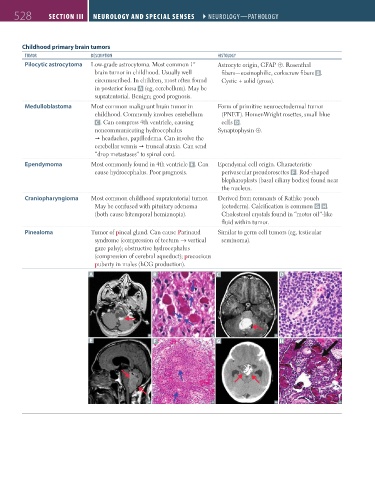
Childhood primary brain tumors
tumor desCriPtion histology
Pilocytic astrocytoma Low-grade astrocytoma. Most common 1° Astrocyte origin, GFAP ⊕. Rosenthal
brain tumor in childhood. Usually well fibers—eosinophilic, corkscrew fibers B .
circumscribed. In children, most often found Cystic + solid (gross).
in posterior fossa A (eg, cerebellum). May be
supratentorial. Benign; good prognosis.
Medulloblastoma Most common malignant brain tumor in Form of primitive neuroectodermal tumor
childhood. Commonly involves cerebellum (PNET). Homer-Wright rosettes, small blue
C . Can compress 4th ventricle, causing cells D.
noncommunicating hydrocephalus Synaptophysin ⊕.
headaches, papilledema. Can involve the
cerebellar vermis truncal ataxia. Can send
“drop metastases” to spinal cord.
Ependymoma Most commonly found in 4th ventricle E . Can Ependymal cell origin. Characteristic
cause hydrocephalus. Poor prognosis. perivascular pseudorosettes F . Rod-shaped
blepharoplasts (basal ciliary bodies) found near
the nucleus.
Craniopharyngioma Most common childhood supratentorial tumor. Derived from remnants of Rathke pouch
May be confused with pituitary adenoma (ectoderm). Calcification is common G H.
(both cause bitemporal hemianopia). Cholesterol crystals found in “motor oil”-like
fluid within tumor.
Pinealoma Tumor of pineal gland. Can cause Parinaud Similar to germ cell tumors (eg, testicular
syndrome (compression of tectum → vertical seminoma).
gaze palsy); obstructive hydrocephalus
(compression of cerebral aqueduct); precocious
puberty in males (hCG production).
A B C D
E F G H
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 528 11/8/19 7:39 AM