Page 574 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 574
530 SecTioN iii Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology
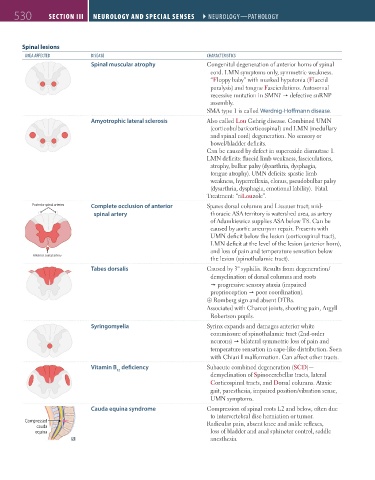
Spinal lesions
AreA AFFeCted diseAse ChArACteristiCs
Spinal muscular atrophy Congenital degeneration of anterior horns of spinal
cord. LMN symptoms only, symmetric weakness.
“Floppy baby” with marked hypotonia (Flaccid
paralysis) and tongue Fasciculations. Autosomal
recessive mutation in SMN1 defective snRNP
assembly.
SMA type 1 is called Werdnig-Hoffmann disease.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Also called Lou Gehrig disease. Combined UMN
(corticobulbar/corticospinal) and LMN (medullary
and spinal cord) degeneration. No sensory or
bowel/bladder deficits.
Can be caused by defect in superoxide dismutase 1.
LMN deficits: flaccid limb weakness, fasciculations,
atrophy, bulbar palsy (dysarthria, dysphagia,
tongue atrophy). UMN deficits: spastic limb
Posterior spinal arteries
weakness, hyperreflexia, clonus, pseudobulbar palsy
(dysarthria, dysphagia, emotional lability). Fatal.
Posterior spinal arteries Treatment: “riLouzole”.
Posterior spinal arteries
Posterior spinal arteries
Posterior spinal arteries Complete occlusion of anterior Spares dorsal columns and Lissauer tract; mid-
Posterior spinal arteries
spinal artery thoracic ASA territory is watershed area, as artery
of Adamkiewicz supplies ASA below T8. Can be
Anterior spinal artery caused by aortic aneurysm repair. Presents with
UMN deficit below the lesion (corticospinal tract),
Anterior spinal artery LMN deficit at the level of the lesion (anterior horn),
Anterior spinal artery
Anterior spinal artery
and loss of pain and temperature sensation below
Anterior spinal artery
Anterior spinal artery the lesion (spinothalamic tract).
Tabes dorsalis Caused by 3° syphilis. Results from degeneration/
demyelination of dorsal columns and roots
progressive sensory ataxia (impaired
proprioception poor coordination).
⊕ Romberg sign and absent DTRs.
Associated with Charcot joints, shooting pain, Argyll
Robertson pupils.
Syringomyelia Syrinx expands and damages anterior white
commissure of spinothalamic tract (2nd-order
neurons) bilateral symmetric loss of pain and
temperature sensation in cape-like distribution. Seen
with Chiari I malformation. Can affect other tracts.
Vitamin B deficiency Subacute combined degeneration (SCD)—
12
demyelination of Spinocerebellar tracts, lateral
Corticospinal tracts, and Dorsal columns. Ataxic
gait, paresthesia, impaired position/vibration sense,
UMN symptoms.
Cauda equina syndrome Compression of spinal roots L2 and below, often due
to intervertebral disc herniation or tumor.
Compressed Radicular pain, absent knee and ankle reflexes,
cauda
equina loss of bladder and anal sphincter control, saddle
anesthesia.
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 530 11/8/19 7:39 AM