Page 573 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 573
Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PAthology SecTioN iii 529
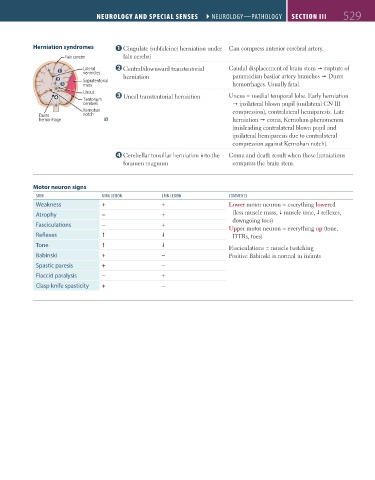
Herniation syndromes Cingulate (subfalcine) herniation under Can compress anterior cerebral artery.
Falx cerebri falx cerebri
Lateral Central/downward transtentorial Caudal displacement of brain stem rupture of
ventricles
herniation paramedian basilar artery branches Duret
Supratentorial
mass hemorrhages. Usually fatal.
Uncus Uncal transtentorial herniation Uncus = medial temporal lobe. Early herniation
Tentorium
cerebelli ipsilateral blown pupil (unilateral CN III
Kernohan compression), contralateral hemiparesis. Late
Duret notch
hemorrhage herniation coma, Kernohan phenomenon
(misleading contralateral blown pupil and
ipsilateral hemiparesis due to contralateral
compression against Kernohan notch).
Cerebellar tonsillar herniation into the Coma and death result when these herniations
foramen magnum compress the brain stem.
Motor neuron signs
sign umn lesion lmn lesion Comments
Weakness + + Lower motor neuron = everything lowered
Atrophy − + (less muscle mass, muscle tone, reflexes,
Fasciculations − + downgoing toes)
Upper motor neuron = everything up (tone,
Reflexes DTRs, toes)
Tone Fasciculations = muscle twitching
Babinski + − Positive Babinski is normal in infants
Spastic paresis + −
Flaccid paralysis − +
Clasp knife spasticity + −
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 529 11/8/19 7:39 AM