Page 180 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 180
The City & Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1
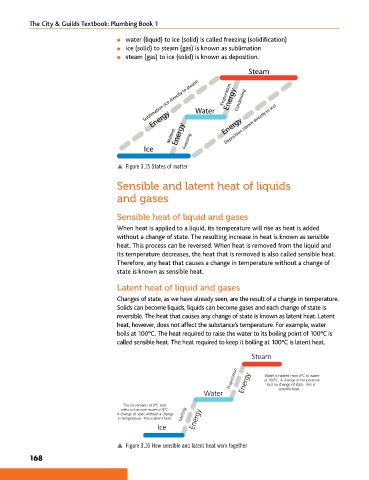
l water (liquid) to ice (solid) is called freezing (solidification)
l ice (solid) to steam (gas) is known as sublimation
l steam (gas) to ice (solid) is known as deposition.
Steam
Sublimation (ice directly to steam) Water Evaporation Energy Condensing
Deposition (steam directly to ice)
Energy
Melting Energy Freezing Energy
Ice
p Figure 3.15 States of matter
Sensible and latent heat of liquids
and gases
Sensible heat of liquid and gases
When heat is applied to a liquid, its temperature will rise as heat is added
without a change of state. The resulting increase in heat is known as sensible
heat. This process can be reversed. When heat is removed from the liquid and
its temperature decreases, the heat that is removed is also called sensible heat.
Therefore, any heat that causes a change in temperature without a change of
state is known as sensible heat.
Latent heat of liquid and gases
Changes of state, as we have already seen, are the result of a change in temperature.
Solids can become liquids, liquids can become gases and each change of state is
reversible. The heat that causes any change of state is known as latent heat. Latent
heat, however, does not affect the substance’s temperature. For example, water
boils at 100°C. The heat required to raise the water to its boiling point of 100°C is
called sensible heat. The heat required to keep it boiling at 100°C is latent heat.
Steam
Evaporation Energy at 100ºC. A change in temperature
Water is heated from 0ºC to water
but no change of state. This is
Water sensible heat.
The ice remains at 0ºC and
melts to become water at 0ºC.
A change of state without a change Melting
in temperature. This is latent heat. Energy
Ice
p Figure 3.16 How sensible and latent heat work together
168
9781510416482.indb 168 29/03/19 8:55 PM