Page 466 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 466
432 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
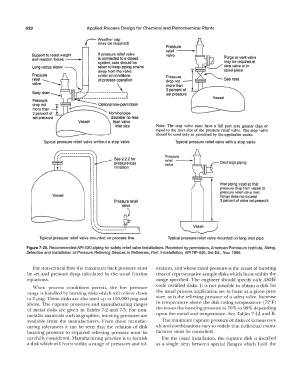
r
Weather cap
(may be required)
Pressure
relief
Support to resist weight If pressure relief valve valve
and reaction forces ---·, is connected to a closed
system, care should be
taken to keep piping strains
away from the valve
under all conditions Pressure
of process operation drop not
\ more than
3 percent of
---------- , I set pressure
---------------------V Vessel
Pressure � nal
drop not low-point drain
more than
3 percent of Nominal pipe
set pressure diameter no less
Vessel than valve
Inlet size Note: The stop valve must have a full port area greater than or
equal to the inlet size of the pressure relief valve. The stop valve
should be used only as permitted by the applicable codes.
Typical pressure relief valve without a stop valve Typical pressure relief valve with a stop valve
: , ,--------------, ' l See 2.2.2 for Pressure
,� pressure-loss relief Discharge piping
valve
limitation
Inlet piping sized so that
pressure drop from vessel to
pressure relief valve inlet
Vessel flange does not exceed
3 percent of valve set pressure
.
I
I
I
I
'
' ....... 1
Typical pressure relief valve mounted on process line Typical pressure relief valve mounted on long inlet pipe
Figure 7-20. Recommended APl-520 piping for safety relief valve installations. Reprinted by permission, American Petroleum Institute, Sizing,
Selection and Installation of Pressure Relieving Devices in Refineries, Part II-Installation, API RP-520, 3rd Ed., Nov. 1988.
For non-critical flow the maximum back pressure must erances, and whose rated pressure is the result of bursting
be set and pressure drop calculated by the usual friction tests of representative sample disks which burst within the
equations. range specified. The engineer should specify only ASME
code certified disks. It is not possible to obtain a disk for
When process conditions permit, the low pressure
range is handled by bursting disks which will relieve down the usual process application set to burst at a given pres-
to 2 psig. These disks are also used up to 100,000 psig and sure, as is the relieving pressure of a safety valve. Increase
above. The rupture pressures and manufacturing ranges in temperature above the disk rating temperature (72°:F)
of metal disks are given in Tables 7-2 and 7-3. For non- decreases the bursting pressure to 70% to 90% depending
metallic materials such as graphite, bursting pressures are upon the metal and temperature. See Tables 7-4A and B.
available from the manufacturers. From these manufac- The minimum rupture pressure of disks of various met-
turing tolerances it can be seen that the relation of disk als and combinations vary so widely that individual manu-
bursting pressure to required relieving pressure must be facturer must be consulted.
carefully considered. Manufacturing practice is to furnish For the usual installation, the rupture disk is installed
a disk which will burst within a range of pressures and tol- as a single item between special flanges which hold the