Page 81 - C:\Users\trainee\AppData\Local\Temp\msoEAA3.tmp
P. 81
Document Title
Fundamentals of Stress and Vibration 2. Engineering Mechanics Chapter
[A Practical guide for aspiring Designers / Analysts]
Solution: for a general curve the radius of curvature varies from point to point, as shown in
[Fig 2.66] and is attributed to the fact that, both slope and the rate of change of slope vary form
point to point.
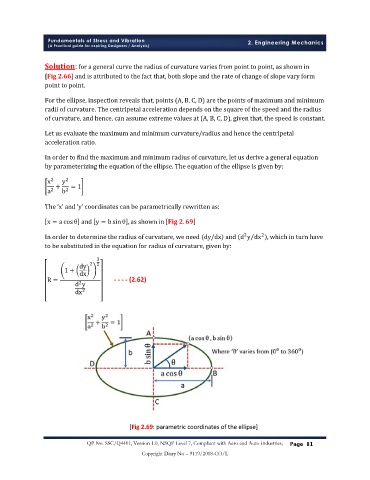
For the ellipse, inspection reveals that, points (A, B, C, D) are the points of maximum and minimum
radii of curvature. The centripetal acceleration depends on the square of the speed and the radius
of curvature, and hence, can assume extreme values at (A, B, C, D), given that, the speed is constant.
Let us evaluate the maximum and minimum curvature/radius and hence the centripetal
acceleration ratio.
In order to find the maximum and minimum radius of curvature, let us derive a general equation
by parameterizing the equation of the ellipse. The equation of the ellipse is given by:
x 2 y 2
+ = 1
a 2 b 2
The ‘x’ and ‘y’ coordinates can be parametrically rewritten as:
x = a cos θ and y = b sinθ , as shown in .
2
2
In order to determine the radius of curvature, we need (dy/dx) and d y dx , which in turn have
to be substituted in the equation for radius of curvature, given by:
3
dy 2 2
1 + dx
R = - - - - (2.62)
2
d y
dx 2
[Fig 2.69: parametric coordinates of the ellipse]
QP No. SSC/Q4401, Version 1.0, NSQF Level 7, Compliant with Aero and Auto Industries, P
Page 81 age 81
Copyright Diary No – 9119/2018-CO/L