Page 113 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 113
CHAPTER 12: Rapid Response Teams 81
100
AM round PM round
90
Number of MET calls per half hour 70 Observations
80
60
50
40
30
20
Decreased
10
0 observations
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23
Time of day (hours)
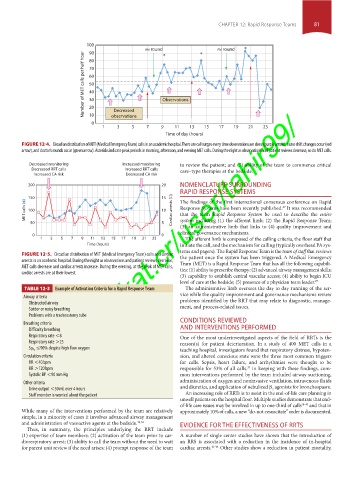
FIGURE 12-4. Circadian distribution of MET (Medical Emergency Team) calls in an academic hospital. There are call surges every time observations are done (purple arrow), nurse shift changes occur (red
arrow), and doctor’s rounds occur (green arrow). Asterisks indicate peak periods in morning, afternoon, and evening MET calls. During the night as observations and patient reviews decrease, so do MET calls.
Decreased monitoring Increased monitoring to review the patient; and (5) ability of the team to commence critical
Decreased RRT calls Increased RRT calls care–type therapies at the bedside.
Increased CA risk Decreased CA risk
200 20 NOMENCLATURE SURROUNDING
RAPID RESPONSE SYSTEMS
150 15 The findings of the first international consensus conference on Rapid
MET calls ( ) 100 10 Cardiac arrests ( ) Response Systems have been recently published. It was recommended
27
that the term Rapid Response System be used to describe the entire
50 5 system including (1) the afferent limb; (2) the Rapid Response Team;
(3) an administrative limb that links to (4) quality improvement and
clinical governance mechanisms.
0 https://kat.cr/user/tahir99/
0
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 The afferent limb is composed of the calling criteria, the floor staff that
Time (hours) initiate the call, and the mechanism for calling (typically overhead PA sys-
tems and pagers). The Rapid Response Team is the team of staff that reviews
FIGURE 12-5. Circadian distribution of MET (Medical Emergency Team) calls and cardiac the patient once the system has been triggered. A Medical Emergency
arrests in an academic hospital. During the night as observations and patient reviews decrease, Team (MET) is a Rapid Response Team that has all the following capabili-
MET calls decrease and cardiac arrests increase. During the evening, at the peak of MET calls, ties: (1) ability to prescribe therapy; (2) advanced airway management skills;
cardiac arrests are at their lowest.
(3) capability to establish central vascular access; (4) ability to begin ICU
level of care at the bedside; (5) presence of a physician team leader. 27
TABLE 12-3 Example of Activation Criteria for a Rapid Response Team The administrative limb oversees the day to day running of the ser-
vice while the quality improvement and governance mechanisms review
Airway criteria problems identified by the RRT that may relate to diagnostic, manage-
Obstructed airway
Stridor or noisy breathing ment, and process-related issues.
Problems with a tracheostomy tube
Breathing criteria CONDITIONS REVIEWED
Difficulty breathing AND INTERVENTIONS PERFORMED
Respiratory rate <8 One of the most underinvestigated aspects of the field of RRTs is the
Respiratory rate >25 reason(s) for patient deterioration. In a study of 400 MET calls in a
≤90% despite high flow oxygen
Sp O 2 teaching hospital, investigators found that respiratory distress, hypoten-
Circulation criteria sion, and altered conscious state were the three most common triggers
HR <40 bpm for calls. Sepsis, heart failure, and arrhythmias were thought to be
37
HR >120 bpm responsible for 53% of all calls. In keeping with these findings, com-
Systolic BP <90 mm Hg mon interventions performed by the team included airway suctioning,
Other criteria administration of oxygen and noninvasive ventilation, intravenous fluids
Urine output <50 mL over 4 hours and diuretics, and application of nebulized β agonists for bronchospasm.
2
Staff member is worried about the patient An increasing role of RRTs is to assist in the end-of-life care planning in
unwell patients on the hospital floor. Multiple studies demonstrate that end-
of-life care issues may be involved in up to one-third of calls 38-40 and that in
While many of the interventions performed by the team are relatively approximately 10% of calls, a new “do-not-resuscitate” order is documented.
simple, in a minority of cases it involves advanced airway management
and administration of vasoactive agents at the bedside. 34,36 EVIDENCE FOR THE EFFECTIVENESS OF RRTS
Thus, in summary, the principles underlying the RRT include
(1) expertise of team members; (2) activation of the team prior to car- A number of single center studies have shown that the introduction of
diorespiratory arrest; (3) ability to call the team without the need to wait an RRS is associated with a reduction in the incidence of in-hospital
for parent unit review if the need arises; (4) prompt response of the team cardiac arrests. 41-44 Other studies show a reduction in patient mortality,
Section01.indd 81 1/22/2015 9:37:19 AM