Page 289 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 289
CHAPTER 28: Interpretation of Hemodynamic Waveforms 193
is located in a vessel whose capillary bed supplies an area of markedly
reduced alveolar ventilation. 20,38 Second, an initial 15 to 20 mL of “dead
space” blood should be withdrawn and discarded before the sample
for analysis is obtained, to reduce the likelihood of obtaining a false-
negative result when the inflated catheter has truly wedged. Finally, a
38
BALLOON false-positive result (ie, high O saturation in aspirated blood when the
2
INFLATED catheter is not wedged) can occur if the sample is aspirated too quickly.
Ppa It is recommended that the sample be aspirated at a rate no faster than
– 60 – 3 mL/min. 38
Partial Ppw
– 40 – RESPIRATORY INFLUENCES: TRANSMURAL PRESSURE
28
– 20 – The Pra and Ppw are used as surrogates for RV and LV filling pressure,
respectively. However, it is transmural (intravascular minus pleural)
pressure that represents the distending pressure for cardiac filling.
– 0 –
During normal breathing, pleural pressure (Ppl) is slightly negative at
end-expiration and intrathoracic vascular pressures measured at this
point in respiratory cycle provide the best estimate of transmural pres-
sure (Fig. 28-16). Either a strip recording or the cursor method should
be used to define the end-expiratory pressure.
One error is the assumption that during mechanical ventilation the
lowest point in the pressure tracing reflects end expiration. While this
BALLOON is true during controlled ventilation, inspiratory efforts that trigger
INFLATED mechanical breaths produce a nadir in the pressure tracing (Fig. 28-16).
Ppa Identification of end expiration in the Ppw tracing is aided by the knowl-
– 60 – edge that expiration is usually longer than inspiration, two exceptions
being marked tachypnea and inverse-ratio ventilation. Identification of
– 40 – Ppw end expiration from the pressure tracing should not be difficult when
interpreted in relationship to the patient’s ventilatory pattern. When
confusion occurs, a simultaneous airway pressure tracing may be used.
– 20 – A C V The Pra and Ppw will overestimate transmural pressure if intrathoracic
12 pressure is positive at end expiration. This can occur from an increase in
X X’ Y
– 0 – end-expiratory lung volume due to applied positive end-expiratory pres-
sure (PEEP) or auto-PEEP, or from increased intra-abdominal pressure
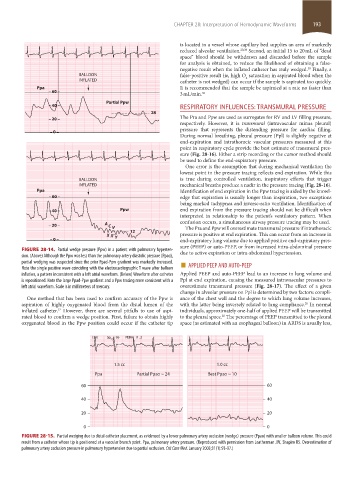
FIGURE 28-14. Partial wedge pressure (Ppw) in a patient with pulmonary hyperten- due to active expiration or intra-abdominal hypertension.
sion. (Above) Although the Ppw was less than the pulmonary artery diastolic pressure (Ppad),
partial wedging was suspected since the prior Ppad-Ppw gradient was markedly increased. ■
Note the single positive wave coinciding with the electrocardiographic T wave after balloon APPLIED PEEP AND AUTO-PEEP
inflation, a pattern inconsistent with a left atrial waveform. (Below) Waveform after catheter Applied PEEP and auto-PEEP lead to an increase in lung volume and
is repositioned. Note the large Ppad-Ppw gradient and a Ppw tracing more consistent with a Ppl at end expiration, causing the measured intravascular pressures to
left atrial waveform. Scale is in millimeters of mercury. overestimate transmural pressure (Fig. 28-17). The effect of a given
change in alveolar pressure on Ppl is determined by two factors: compli-
One method that has been used to confirm accuracy of the Ppw is ance of the chest wall and the degree to which lung volume increases,
aspiration of highly oxygenated blood from the distal lumen of the with the latter being inversely related to lung compliance. In normal
20
inflated catheter. However, there are several pitfalls to use of aspi- individuals, approximately one-half of applied PEEP will be transmitted
37
rated blood to confirm a wedge position. First, failure to obtain highly to the pleural space. The percentage of PEEP transmitted to the pleural
20
oxygenated blood in the Ppw position could occur if the catheter tip space (as estimated with an esophageal balloon) in ARDS is usually less,
(34) Sp 96 PERH 0 . 2
O 2
1.5 cc 1.0 cc
Ppa Partial Ppao ~ 24 Best Ppao ~ 10
60 60
40 40
20 20
0 0
FIGURE 28-15. Partial wedging due to distal catheter placement, as evidenced by a lower pulmonary artery occlusion (wedge) pressure (Ppao) with smaller balloon volume. This could
result from a catheter whose tip is positioned at a vascular branch point. Ppa, pulmonary artery pressure. (Reproduced with permission from Leatherman JW, Shapiro RS. Overestimation of
pulmonary artery occlusion pressure in pulmonary hypertension due to partial occlusion. Crit Care Med. January 2003;31(1):93-97.)
section02.indd 193 1/13/2015 2:05:34 PM