Page 417 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 417
CHAPTER 36: Cardiac Arrhythmias, Pacing, Cardioversion, and Defibrillation in the Critical Care Setting 287
preexcitation is not manifest on the ECG and retrograde conduction via function. In some instances, a transesophageal echocardiogram may be
the accessory connection is concealed. True atrial tachycardia is most required to assess valve function or to determine if an intracardiac throm-
commonly due to enhanced or abnormal atrial automaticity or triggered bus is present (usually for atrial fibrillation or flutter). Cardiac hemody-
activity. P waves usually precede each QRS complex unless there is AV namic data during the arrhythmia, if available, should be reviewed.
conduction block. Multifocal atrial tachycardia is characterized by varia-
tion in P-wave morphology on a beat-to-beat basis. ■ MANAGEMENT OF SUPRAVENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTHMIAS
■ EVALUATION OF THE PATIENT WITH SUPRAVENTRICULAR General Principles of Treatment: Sinus rhythm should be restored as
soon as possible if the patient is symptomatic. In the case of AF, therapy
TACHYARRHYTHMIA aimed at controlling the ventricular rate is usually the initial approach.
The initial evaluation of the patient with a sustained supraventricular Any reversible causes should be identified and corrected. Underlying
structural heart disease should be treated—particularly the manage-
tachyarrhythmia should include a thorough history (if patient able to ment of ischemic heart disease, left ventricular dysfunction, and/or
communicate) and physical examination with special attention to detect- hypertension should be optimized. The probability of recurrence and
ing structural heart disease. A 12-lead ECG of the arrhythmia as well the need for chronic prophylactic therapy should be determined.
16
as during sinus rhythm should be obtained. Rhythm strips documenting
onset and termination of the arrhythmia should be reviewed. Laboratory AF/Atrial Flutter: The therapeutic approach for the management of
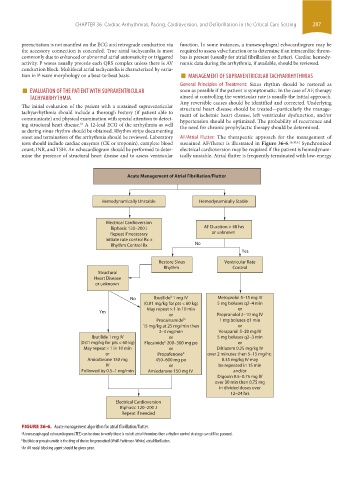
tests should include cardiac enzymes (CK or troponin), complete blood sustained AF/flutter is illustrated in Figure 36-6. 16,40,44 Synchronized
count, INR, and TSH. An echocardiogram should be performed to deter- electrical cardioversion may be required if the patient is hemodynam-
mine the presence of structural heart disease and to assess ventricular ically unstable. Atrial flutter is frequently terminated with low-energy
Acute Management of Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter
Hemodynamically Unstable Hemodynamically Stable
Electrical Cardioversion
Biphasic 120–200 J AF Duration > 48 hrs
Repeat if necessary or unknown
Initiate rate control Rx ±
Rhythm Control Rx No
Yes
Restore Sinus Ventricular Rate
Rhythm Control
Structural
Heart Disease
or unknown
a
No Ibutilide 1 mg IV Metoprolol 5–15 mg IV
(0.01 mg/kg for pts < 60 kg) 5 mg boluses q2–4 min
May repeat × 1 in 10 min or
Yes
or Propranolol 2–10 mg IV
Procainamide b 1 mg boluses q1 min
15 mg/kg at 25 mg/min then or
2–4 mg/min Verapamil 5–20 mg IV
Ibutilide 1 mg IV or 5 mg boluses q2–3 min
c
(0.01 mg/kg for pts < 60 kg) Flecainide 200–300 mg po or
May repeat × 1 in 10 min or Diltiazem 0.25 mg/kg IV
or Propafenone c over 2 minutes then 5–15 mg/hr;
Amiodarone 150 mg 450–600 mg po 0.35 mg/kg IV may
IV or be repeated in 15 min
Followed by 0.5–1 mg/min Amiodarone 150 mg IV and/or
Digoxin 0.5–0.75 mg IV
over 30 min then 0.75 mg
in divided doses over
12–24 hrs
Electrical Cardioversion
Biphasic 120–200 J
Repeat if needed
FIGURE 36-6. Acute management algorithm for atrial fibrillation/flutter.
a A transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) can be done to verify there is no left atrial thrombus then a rhythm control strategy can still be pursued.
b Ibutilide or procainamide is the drug of choice for preexcited (Wolf-Parkinson-White) atrial fibrillation.
c An AV nodal blocking agent should be given prior.
section03.indd 287 1/23/2015 2:07:13 PM