Page 124 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 124
Plate 4-39 Integumentary System
KERATOSIS PILARIS
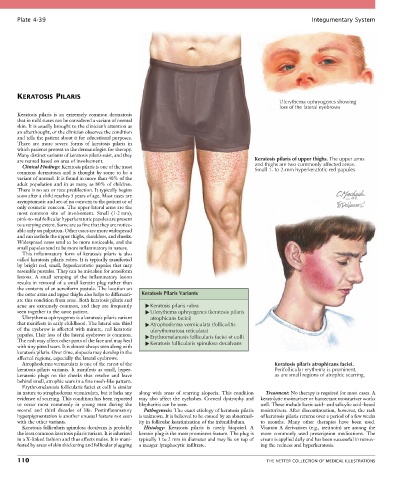
Ulerythema ophryogenes showing
loss of the lateral eyebrows
Keratosis pilaris is an extremely common dermatosis
that in mild states can be considered a variant of normal
skin. It is usually brought to the clinician’s attention as
an afterthought, or the clinician observes the condition
and tells the patient about it for educational purposes.
There are more severe forms of keratosis pilaris in
which patients present to the dermatologist for therapy.
Many distinct variants of keratosis pilaris exist, and they
are named based on area of involvement. Keratosis pilaris of upper thighs. The upper arms
Clinical Findings: Keratosis pilaris is one of the most and thighs are two commonly affected areas.
common dermatoses and is thought by some to be a Small 1- to 2-mm hyperkeratotic red papules
variant of normal. It is found in more than 40% of the
adult population and in as many as 80% of children.
There is no sex or race predilection. It typically begins
soon after a child reaches 5 years of age. Most cases are
asymptomatic and are of no concern to the patient or of
only cosmetic concern. The upper lateral arms are the
most common site of involvement. Small (1-2 mm),
pink-to-red follicular hyperkeratotic papules are present
to a varying extent. Some are so fine that they are notice-
able only on palpation. Other cases are more widespread
and can include the upper thighs, shoulders, and cheeks.
Widespread cases tend to be more noticeable, and the
small papules tend to be more inflammatory in nature.
This inflammatory form of keratosis pilaris is also
called keratosis pilaris rubra. It is typically manifested
by bright red, small, hyperkeratotic papules that may
resemble pustules. They can be mistaken for acneiform
lesions. A small scraping of the inflammatory lesion
results in removal of a small keratin plug rather than
the contents of an acneiform pustule. The location on
the outer arms and upper thighs also helps to differenti- Keratosis Pilaris Variants
ate this condition from acne. Both keratosis pilaris and
acne are extremely common, and they are frequently Keratosis pilaris rubra
seen together in the same patient. Ulerythema ophryogenes (keratosis pilaris
Ulerythema ophryogenes is a keratosis pilaris variant atrophicans faciei)
that manifests in early childhood. The lateral one third Atrophoderma vermiculata (folliculitis
of the eyebrow is affected with minute, red keratotic ulerythematosa reticulata)
papules. Hair loss of the lateral eyebrows is common. Erythromelanosis follicularis faciei et colli
The rash may affect other parts of the face and may heal Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans
with tiny pitted scars. It is almost always seen along with
keratosis pilaris. Over time, alopecia may develop in the
affected regions, especially the lateral eyebrows.
Atrophoderma vermiculata is one of the rarest of the Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei.
keratosis pilaris variants. It manifests as small, hyper- Perifollicular erythema is prominent,
keratotic plugs on the cheeks that resolve and leave as are small regions of atrophic scarring.
behind small, atrophic scars in a fine mesh-like pattern.
Erythromelanosis follicularis faciei et colli is similar
in nature to atrophoderma vermiculata, but it lacks any along with areas of scarring alopecia. This condition Treatment: No therapy is required for most cases. A
evidence of scarring. This condition has been reported may also affect the eyelashes. Corneal dystrophy and keratolytic moisturizer or humectant moisturizer works
to occur most commonly in young men during the blepharitis can be seen. well. These include lactic acid– and salicylic acid–based
second and third decades of life. Postinflammatory Pathogenesis: The exact etiology of keratosis pilaris moisturizers. After discontinuation, however, the rash
hyperpigmentation is another unusual feature not seen is unknown. It is believed to be caused by an abnormal- of keratosis pilaris returns over a period of a few weeks
with the other variants. ity in follicular keratinization of the infundibulum. to months. Many other therapies have been used.
Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans is probably Histology: Keratosis pilaris is rarely biopsied. A Vitamin A derivatives (e.g., tretinoin) are among the
the least common keratosis pilaris variant. It is inherited keratin plug is the most prominent feature. The plug is more commonly used prescription medications. The
in a X-linked fashion and thus affects males. It is mani- typically 1 to 2 mm in diameter and may lie on top of cream is applied daily and has been successful in remov-
fested by areas of skin thickening and follicular plugging a meager lymphocytic infiltrate. ing the redness and hyperkeratosis.
110 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS