Page 138 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 138
Plate 4-53 Integumentary System
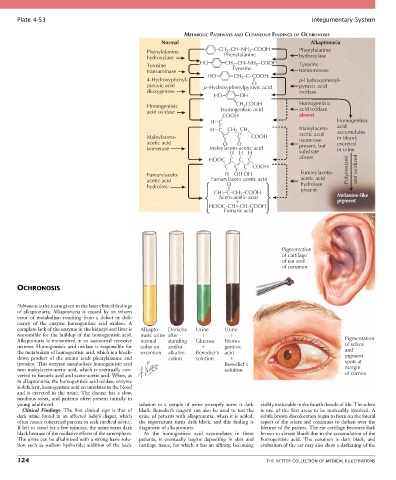
METABOLIC PATHWAYS AND CUTANEOUS FINDINGS OF OCHRONOSIS
Normal Alkaptonuria
2
Phenylalanine –CH 2 –CH–NH –COOH Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine
hydroxylase hydroxylase
HO CH –CH–NH –COOH
2
Tyrosine Tyrosine 2 Tyrosine
transaminase transaminase
HO CH –C–COOH
4-Hydroxyphenyl- 2 p-Hydroxyphenyl-
O
pyruvic acid p–Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid pyruvic acid
dioxygenase oxidase
HO OH
CH COOH
2
Homogentisic Homogentisic acid Homogentisic
acid oxidase
acid oxidase
_ COOH absent
H C Homogentisic
acid
H C CH CH _ 2 Maleylaceto- accumulates
2
_
Maleylaceto- C _ C COOH acetic acid in blood;
isomerase
acetic acid O O present, but excreted
isomerase Maleylaceto-acetic acid in urine
H H H _ substrate
_
_
HOOC C C _ C absent
_ C _ _ Polymerized and oxidized
_ _ C _ C COOH
Fumarylaceto- H OH OH Fumarylaceto-
acetic acid Fumarylaceto-acetic acid acetic acid
hydrolase O hydrolase
CH –C–CH –COOH present Melanine-like
2
3
Aceto-acetic acid
pigment
HOOC–CH CH–COOH
Fumaric acid
Pigmentation
of cartilage
of ear and
of cerumen
OCHRONOSIS
Ochronosis is the name given to the later clinical findings
of alkaptonuria. Alkaptonuria is caused by an inborn
error of metabolism resulting from a defect or defi-
ciency of the enzyme homogentisic acid oxidase. A
complete lack of the enzyme in the kidneys and liver is Alkapto- Darkens Urine Urine
responsible for the buildup of the homogentisic acid. nuric urine after
Alkaptonuria is transmitted in an autosomal recessive normal standing Glucose Homo- Pigmentation
manner. Homogentisic acid oxidase is responsible for color on and/or gentisic of sclera
the metabolism of homogentisic acid, which is a break- excretion alkalini- Benedict’s acid and
down product of the amino acids phenylalanine and zation solution pigment
tyrosine. This enzyme metabolizes homogentisic acid Benedict’s spots at
into maleylaceto-acetic acid, which is eventually con- solution margin
verted to fumaric acid and aceto-acetic acid. When, as of cornea
in alkaptonuria, the homogentisic acid oxidase enzyme
is deficient, homogentisic acid accumulates in the blood
and is excreted in the urine. The disease has a slow,
insidious onset, and patients often present initially in
young adulthood. solution to a sample of urine promptly turns it dark visibly noticeable in the fourth decade of life. The sclera
Clinical Findings: The first clinical sign is that of black. Benedict’s reagent can also be used to test the is one of the first areas to be noticeably involved. A
dark urine found in an affected baby’s diaper, which urine of patients with alkaptonuria; when it is added, subtle brown discoloration begin to form on the lateral
often causes concerned parents to seek medical advice. the supernatant turns dark black, and this finding is aspect of the sclera and continues to darken over the
If left to stand for a few minutes, the urine turns dark diagnostic of alkaptonuria. lifetime of the patient. The ear cartilage becomes dark
black because of the oxidative effects of the atmosphere. As the homogentisic acid accumulates in these brown to almost bluish due to the accumulation of the
The urine can be alkalinized with a strong basic solu- patients, it eventually begins depositing in skin and homogentisic acid. The cerumen is dark black, and
tion such as sodium hydroxide; addition of the basic cartilage tissue, for which it has an affinity, becoming evaluation of the ear may also show a darkening of the
124 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS