Page 164 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 164
Plate 5-1 Integumentary System
BASEMENT MEMBRANE ZONE AND HEMIDESMOSOME
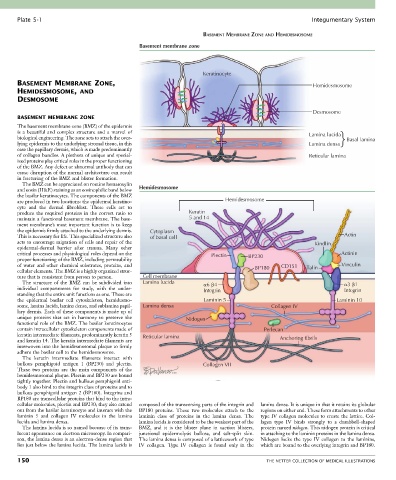
Basement membrane zone
Keratinocyte
BASEMENT MEMBRANE ZONE, Hemidesmosome
HEMIDESMOSOME, AND
DESMOSOME
Desmosome
BASEMENT MEMBRANE ZONE
The basement membrane zone (BMZ) of the epidermis
is a beautiful and complex structure and a marvel of Lamina lucida
biological engineering. The zone acts to attach the over- Basal lamina
lying epidermis to the underlying stromal tissue, in this Lamina densa
case the papillary dermis, which is made predominantly
of collagen bundles. A plethora of unique and special- Reticular lamina
ized proteins play critical roles in the proper functioning
of the BMZ. Any defect or abnormal antibody that can
cause disruption of the normal architecture can result
in fracturing of the BMZ and blister formation.
The BMZ can be appreciated on routine hematoxylin
and eosin (H&E) staining as an eosinophilic band below Hemidesmosome
the basilar keratinocytes. The components of the BMZ
are produced in two locations: the epidermal keratino- Hemidesmosome
cyte and the dermal fibroblast. These cells act to
produce the required proteins in the correct ratio to Keratin
maintain a functional basement membrane. The base- 5 and 14
ment membrane’s most important function is to keep
the epidermis firmly attached to the underlying dermis. Cytoplasm
This is necessary for life. This specialized structure also of basal cell Actin
acts to encourage migration of cells and repair of the Kindlin
epidermal-dermal barrier after trauma. Many other
critical processes and physiological roles depend on the Plectin BP230 Actinin
proper functioning of the BMZ, including permeability
of water and other chemical substrates, proteins, and BP180 CD151 Talin Vinculin
cellular elements. The BMZ is a highly organized struc-
ture that is consistent from person to person. Cell membrane
The structure of the BMZ can be subdivided into Lamina lucida 6 4 3 1
individual compartments for study, with the under- Integrin Integrin
standing that the entire unit functions as one. These are
the epidermal basilar cell cytoskeleton, hemidesmo- Laminin 5 Laminin 10
some, lamina lucida, lamina densa, and sublamina papil- Lamina densa Collagen IV
lary dermis. Each of these components is made up of
unique proteins that act in harmony to preserve the Nidogen
functional role of the BMZ. The basilar keratinocytes
contain intracellular cytoskeleton components made of Perlecan
keratin intermediate filaments, predominantly keratin 5 Reticular lamina
and keratin 14. The keratin intermediate filaments are Anchoring fibrils
interwoven into the hemidesmosomal plaque to firmly
adhere the basilar cell to the hemidesmosome.
The keratin intermediate filaments interact with
bullous pemphigoid antigen 1 (BP230) and plectin. Collagen VII
These two proteins are the main components of the
hemidesmosomal plaque. Plectin and BP230 are bound
tightly together. Plectin and bullous pemphigoid anti-
body 1 also bind to the integrin class of proteins and to
bullous pemphigoid antigen 2 (BP180). Integrins and
BP180 are transcellular proteins that bind to the intra-
cellular molecules, plectin and BP230; they also extend composed of the transversing parts of the integrin and lamina densa. It is unique in that it retains its globular
out from the basilar keratinocyte and interact with the BP180 proteins. These two molecules attach to the regions on either end. These form attachments to other
laminin 5 and collagen IV molecules in the lamina laminin class of proteins in the lamina densa. The type IV collagen molecules to create the lattice. Col-
lucida and lamina densa. lamina lucida is considered to be the weakest part of the lagen type IV binds strongly to a dumbbell-shaped
The lamina lucida is so named because of its trans- BMZ, and it is the blister plane in suction blisters, protein named nidogen. This nidogen protein is critical
lucent appearance on electron microscopy. In compari- junctional epidermolysis bullosa, and salt-split skin. in attaching to the laminin proteins in the lamina densa.
son, the lamina densa is an electron-dense region that The lamina densa is composed of a latticework of type Nidogen locks the type IV collagen to the laminins,
lies just below the lamina lucida. The lamina lucida is IV collagen. Type IV collagen is found only in the which are bound to the overlying integrin and BP180.
150 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS