Page 165 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 165
Plate 5-2 Autoimmune Blistering Diseases
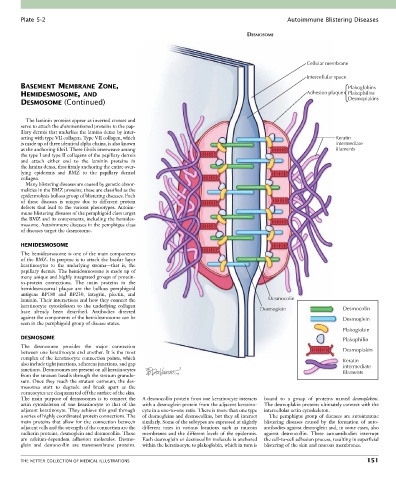
DESMOSOME
Cellular membrane
Intercellular space
BASEMENT MEMBRANE ZONE, Plakoglobins
HEMIDESMOSOME, AND Adhesion plaque Plakophilins
DESMOSOME (Continued) Desmoplakins
The laminin proteins appear as inverted crosses and
serve to attach the aforementioned proteins to the pap-
illary dermis that underlies the lamina densa by inter-
acting with type VII collagen. Type VII collagen, which Keratin
is made up of three identical alpha chains, is also known intermediate
as the anchoring fibril. These fibrils interweave among filaments
the type I and type II collagens of the papillary dermis
and attach either end to the laminin proteins in
the lamina densa, thus firmly anchoring the entire over-
lying epidermis and BMZ to the papillary dermal
collagen.
Many blistering diseases are caused by genetic abnor-
malities in the BMZ proteins; these are classified as the
epidermolysis bullosa group of blistering diseases. Each
of these diseases is unique due to different protein
defects that lead to the various phenotypes. Autoim-
mune blistering diseases of the pemphigoid class target
the BMZ and its components, including the hemides-
mosome. Autoimmune diseases in the pemphigus class
of diseases target the desmosome.
HEMIDESMOSOME
The hemidesmosome is one of the main components
of the BMZ. Its purpose is to attach the basilar layer
keratinocytes to the underlying stroma—that is, the
papillary dermis. The hemidesmosome is made up of
many unique and highly integrated groups of protein-
to-protein connections. The main proteins in the
hemidesmosomal plaque are the bullous pemphigoid
antigens BP180 and BP230, integrin, plectin, and
laminin. Their interactions and how they connect the Desmocolin
keratinocyte cytoskeleton to the underlying collagen Desmocolin
have already been described. Antibodies directed Desmoglein
against the components of the hemidesmosome can be Desmoglein
seen in the pemphigoid group of disease states.
Plakoglobin
DESMOSOME Plakophilin
The desmosome provides the major connection
between one keratinocyte and another. It is the most Desmoplakin
complex of the keratinocyte connection points, which Keratin
also include tight junctions, adherens junctions, and gap intermediate
junctions. Desmosomes are present on all keratinocytes filaments
from the stratum basalis through the stratum granulo-
sum. Once they reach the stratum corneum, the des-
mosomes start to degrade and break apart as the
corneocytes are desquamated off the surface of the skin.
The main purpose of desmosomes is to connect the A desmocollin protein from one keratinocyte interacts bound to a group of proteins named desmoplakins.
actin cytoskeleton of one keratinocyte to that of the with a desmoglein protein from the adjacent keratino- The desmoplakin proteins ultimately connect with the
adjacent keratinocyte. They achieve this goal through cyte in a one-to-one ratio. There is more than one type intercellular actin cytoskeleton.
a series of highly coordinated protein connections. The of desmogleins and desmocollins, but they all interact The pemphigus group of diseases are autoimmune
main proteins that allow for the connection between similarly. Some of the subtypes are expressed at slightly blistering diseases caused by the formation of auto-
adjacent cells and the strength of the connection are the different rates in various locations such as mucous antibodies against desmoglein and, in some cases, also
cadherin proteins, desmoglein and desmocollin. These membranes and the different levels of the epidermis. against desmocollin. These autoantibodies interrupt
are calcium-dependent adhesion molecules. Desmo- Each desmoglein or desmocollin molecule is anchored the cell-to-cell adhesion process, resulting in superficial
glein and desmocollin are transmembrane proteins. within the keratinocyte to plakoglobin, which in turn is blistering of the skin and mucous membranes.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 151