Page 196 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 196
Plate 6-21 Integumentary System
MOLLUSCUM CONTAGIOSUM
As its name implies, molluscum contagiosum is a highly
contagious viral infection that has little morbidity. This
infection is most commonly encountered in children.
The diagnosis is made on clinical grounds after inspec-
tion of the characteristic skin findings. When seen in
the genital region of adults, molluscum contagiosum is
considered to be a sexually transmitted disease. This
infection rarely occurs in immunocompetent adults
outside sexual transmission. In adults with no clear evi-
dence of transmission, an evaluation for an immunosup-
pressed state should be undertaken. Patients taking
chronic immunosuppressive medications and those with
the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome are more Magnified view showing typical
prone to infection with molluscum contagiosum. umbilicated lesion
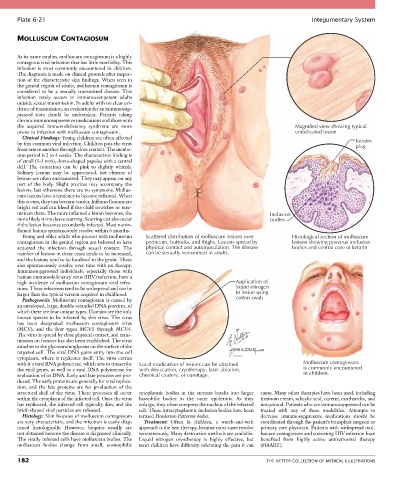
Clinical Findings: Young children are often affected
by this common viral infection. Children pass the virus Keratin
plug
from one to another through close contact. The incuba-
tion period is 2 to 4 weeks. The characteristic finding is
of small (3-5 mm), dome-shaped papules with a central
dell. The coloration can be pink to slightly whitish.
Solitary lesions may be appreciated, but clusters of
lesions are often encountered. They may appear on any
part of the body. Slight pruritus may accompany the
lesions, but otherwise there are no symptoms. Mollus-
cum lesions have a tendency to become inflamed. When
this occurs, they can become tender. Inflamed lesions are
bright red and can bleed if the child scratches or trau-
matizes them. The more inflamed a lesion becomes, the Inclusion
more likely it is to leave scarring. Scarring can also occur bodies
if the lesion becomes secondarily infected. Most nonin-
flamed lesions spontaneously resolve within 6 months.
Young and older adults who present with molluscum Scattered distribution of molluscum lesions over Histological section of molluscum
contagiosum in the genital region are believed to have perineum, buttocks, and thighs. Lesions spread by lesions showing poxvirus inclusion
acquired the infection through sexual contact. The physical contact and autoinoculation. The disease bodies and central core of keratin
number of lesions in these cases tends to be increased, can be sexually transmitted in adults.
and the lesions tend to be localized to the groin. These
also spontaneously resolve over time with no therapy.
Immunosuppressed individuals, especially those with
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, have a
high incidence of molluscum contagiosum viral infec- Application of
tions. These infections tend to be widespread and can be liquid nitrogen
larger than the typical version acquired in childhood. to lesion using
Pathogenesis: Molluscum contagiosum is caused by cotton swab
an enveloped, large, double-stranded DNA poxvirus, of
which there are four unique types. Humans are the only
known species to be infected by this virus. The virus
has been designated molluscum contagiosum virus
(MCV), and the four types MCV1 through MCV4.
The virus is spread by close physical contact, and trans-
mission on fomites has also been established. The virus
attaches to the glycosaminoglycans on the surface of the
targeted cell. The viral DNA gains entry into the cell with
cytoplasm, where it replicates itself. The virus carries E. Hatton
with it a viral RNA polymerase, which acts to transcribe Local eradication of lesions can be obtained Molluscum contagiosum
the viral genes, as well as a viral DNA polymerase for with desiccation, cryotherapy, laser ablation, is commonly encountered
replication of its DNA. Early and late proteins are pro- chemical cautery, or curettage. in children.
duced. The early proteins are generally for viral replica-
tion, and the late proteins are for production of the
structural shell of the virus. These processes all occur cytoplasmic bodies in the stratum basalis into larger cause. Many other therapies have been used, including
within the cytoplasm of the infected cell. Once the virus basophilic bodies in the outer epidermis. As they tretinoin cream, salicylic acid, curette, cantharidin, and
has replicated, the infected cell typically dies, and the enlarge, they often compress the nucleus of the infected imiquimod. Patients who are immunosuppressed can be
brick-shaped viral particles are released. cell. These intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies have been treated with any of these modalities. Attempts to
Histology: Skin biopsies of molluscum contagiosum termed Henderson-Patterson bodies. decrease immunosuppressive medications should be
are very characteristic, and the infection is easily diag- Treatment: Often in children, a watch-and-wait coordinated through the patient’s transplant surgeon or
nosed histologically. However, biopsies usually are approach is the best therapy, because most cases resolve primary care physician. Patients with widespread mol-
not obtained because the disease is diagnosed clinically. spontaneously. Many destructive methods are available. luscum contagiosum and coexisting HIV infection have
The virally infected cells have molluscum bodies. The Liquid nitrogen cryotherapy is highly effective, but benefited from highly active antiretroviral therapy
molluscum bodies change from small, eosinophilic most children have difficulty tolerating the pain it can (HAART).
182 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS