Page 233 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 233
Plate 8-10 Nutritional and Metabolic Diseases
SCURVY (Continued) BONY AND SKIN ABNORMALITIES OF SCURVY
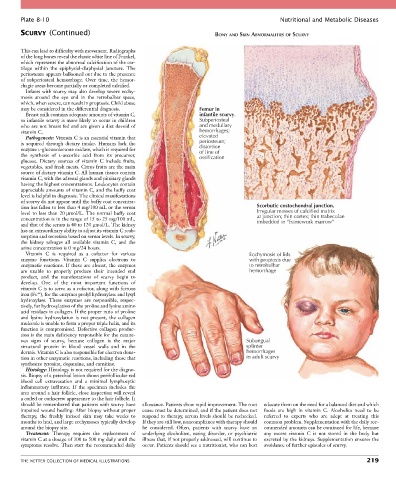
This can lead to difficulty with movement. Radiographs
of the long bones reveal the classic white line of Frankel,
which represents the abnormal calcification of the car-
tilage within the epiphysial-diaphysial juncture. The
periosteum appears ballooned out due to the presence
of subperiosteal hemorrhage. Over time, the hemor-
rhagic areas become partially or completed calcified.
Infants with scurvy may also develop severe ecchy-
mosis around the eye and in the retrobulbar space,
which, when severe, can result in proptosis. Child abuse
may be considered in the differential diagnosis. Femur in
Breast milk contains adequate amounts of vitamin C, infantile scurvy.
so infantile scurvy is more likely to occur in children Subperiosteal
who are not breast fed and are given a diet devoid of and medullary
vitamin C. hemorrhages;
Pathogenesis: Vitamin C is an essential vitamin that elevated
is acquired through dietary intake. Humans lack the periosteum;
enzyme L-gluconolactone oxidase, which is required for distortion
of line of
the synthesis of L-ascorbic acid from its precursor, ossification
glucose. Dietary sources of vitamin C include fruits,
vegetables, and fresh meats. Citrus fruits are the main
source of dietary vitamin C. All human tissues contain
vitamin C, with the adrenal glands and pituitary glands
having the highest concentrations. Leukocytes contain
appreciable amounts of vitamin C, and the buffy coat
level is helpful in diagnosis. The clinical manifestations
of scurvy do not appear until the buffy coat concentra-
tion has fallen to less than 4 mg/100 mL or the serum Scorbutic costochondral junction.
level to less than 20 µmol/L. The normal buffy coat Irregular masses of calcified matrix
concentration is in the range of 15 to 25 mg/100 mL, at junction; thin cortex; thin trabeculae
imbedded in “framework marrow”
and that of the serum is 40 to 120 µmol/L. The kidney
has an extraordinary ability to adjust its vitamin C reab-
sorption and secretion based on serum levels. In scurvy,
the kidney salvages all available vitamin C, and the
urine concentration is 0 mg/24 hours.
Vitamin C is required as a cofactor for various Ecchymosis of lids
enzyme functions. Vitamin C supplies electrons to with proptosis due
enzymatic reactions. If these are absent, the enzymes to retrobulbar
are unable to properly produce their intended end hemorrhage
product, and the manifestations of scurvy begin to
develop. One of the most important functions of
vitamin C is to serve as a cofactor, along with ferrous
++
iron (Fe ), for the enzymes prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl
hydroxylase. These enzymes are responsible, respec-
tively, for hydroxylation of the proline and lysine amino
acid residues in collagen. If the proper ratio of proline
and lysine hydroxylation is not present, the collagen
molecule is unable to form a proper triple helix, and its
function is compromised. Defective collagen produc-
tion is the main deficiency responsible for the cutane-
ous signs of scurvy, because collagen is the major Subungual
structural protein in blood vessel walls and in the splinter
dermis. Vitamin C is also responsible for electron dona- hemorrhages
tion in other enzymatic reactions, including those that in adult scurvy
synthesize tyrosine, dopamine, and carnitine.
Histology: Histology is not required for the diagno-
sis. Biopsy of a petechial lesion shows perifollicular red
blood cell extravasation and a minimal lymphocytic
inflammatory infiltrate. If the specimen includes the
area around a hair follicle, close inspection will reveal
a coiled or corkscrew appearance to the hair follicle. It
should be remembered that patients with scurvy have allowance. Patients show rapid improvement. The root educate them on the need for a balanced diet and which
impaired wound healing: After biopsy without proper cause must be determined, and if the patient does not foods are high in vitamin C. Alcoholics need to be
therapy, the freshly incised skin may take weeks to respond to therapy, serum levels should be rechecked. referred to experts who are adept at treating this
months to heal, and large ecchymoses typically develop If they are still low, noncompliance with therapy should common problem. Supplementation with the daily rec-
around the biopsy site. be considered. Often, patients with scurvy have an ommended amounts can be continued for life, because
Treatment: Therapy requires the replacement of underlying alcoholism, eating disorder, or psychiatric any excess vitamin C is not stored in the body but
vitamin C at a dosage of 300 to 500 mg daily until the illness that, if not properly addressed, will continue to excreted by the kidneys. Supplementation ensures the
symptoms resolve. Then start the recommended daily occur. Patients should see a nutritionist, who can best avoidance of further episodes of scurvy.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 219