Page 231 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 231
Plate 8-8 Nutritional and Metabolic Diseases
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS, HEREDITARY PATTERNS, AND EFFECTS OF PLASMA AND URINARY LEVELS IN PHENYLKETONURIA
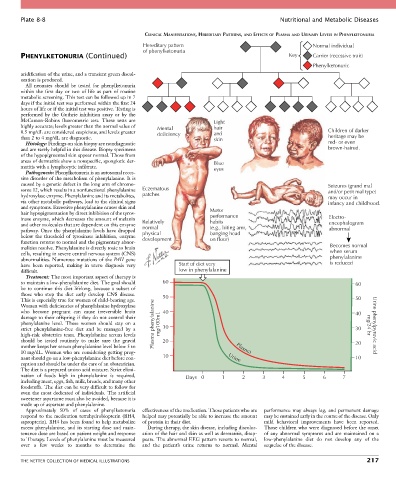
Hereditary pattern Normal individual
of phenylketonuria
PHENYLKETONURIA (Continued) Key Carrier (recessive trait)
Phenylketonuric
acidification of the urine, and a transient green discol-
oration is produced.
All neonates should be tested for phenylketonuria
within the first day or two of life as part of routine
metabolic screening. This test can be followed up in 7
days if the initial test was performed within the first 24
hours of life or if the initial test was positive. Testing is
performed by the Guthrie inhibition assay or by the
McCamon-Robins fluorometric test. These tests are Light
highly accurate; levels greater than the normal value of Mental hair
0.5 mg/dL are considered suspicious, and levels greater deficiency and Children of darker
than 2 to 4 mg/dL are diagnostic. skin heritage may be
Histology: Findings on skin biopsy are nondiagnostic red- or even
and are rarely helpful in this disease. Biopsy specimens brown-haired.
of the hypopigmented skin appear normal. Those from
areas of dermatitis show a nonspecific, spongiotic der- Blue
matitis with a lymphocytic infiltrate. eyes
Pathogenesis: Phenylketonuria is an autosomal reces-
sive disorder of the metabolism of phenylalanine. It is
caused by a genetic defect in the long arm of chromo- Seizures (grand mal
some 12, which results in a nonfunctional phenylalanine Eczematous and/or petit mal type)
hydroxylase enzyme. Phenylalanine and its metabolites, patches may occur in
via other metabolic pathways, lead to the clinical signs infancy and childhood.
and symptoms. Excessive phenylalanine causes skin and Motor
hair hypopigmentation by direct inhibition of the tyros- performance
inase enzyme, which decreases the amount of melanin Relatively habits Electro-
and other molecules that are dependent on this enzyme normal (e.g., biting arm, encephalogram
pathway. Once the phenylalanine levels have dropped physical banging head abnormal
below the threshold of tyrosinase inhibition, enzyme development on floor)
function returns to normal and the pigmentary abnor-
malities resolve. Phenylalanine is directly toxic to brain Becomes normal
cells, resulting in severe central nervous system (CNS) when serum
abnormalities. Numerous mutations of the PAH gene phenylalanine
have been reported, making in utero diagnosis very Start of diet very is reduced
difficult. low in phenylalanine
Treatment: The most important aspect of therapy is
to maintain a low-phenylalanine diet. The goal should 60 60
be to continue this diet lifelong, because a subset of
those who stop the diet early develop CNS disease. 50
This is especially true for women of child-bearing age. 50
Women with deficiencies of phenylalanine hydroxylase
who become pregnant can cause irreversible brain 40 40
damage to their offspring if they do not control their
phenylalanine level. These women should stay on a Plasma phenylalanine mg/100mL mg/24 hr Urine phenylpyruvic acid
strict phenylalanine-free diet and be managed by a 30 30
high-risk obstetrics team. Phenylalanine serum levels
should be tested routinely to make sure the gravid 20 20
mother keeps her serum phenylalanine level below 5 to Plasma
10 mg/dL. Women who are considering getting preg-
nant should go on a low-phenylalanine diet before con- 10 Urine 10
ception and should be under the care of an obstetrician.
The diet is a prepared amino acid mixture. Strict elimi-
nation of foods high in phenylalanine is required, Days 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
including meat, eggs, fish, milk, breads, and many other
foodstuffs. The diet can be very difficult to follow for
even the most dedicated of individuals. The artificial
sweetener aspartame must also be avoided, because it is
made up of aspartate and phenylalanine.
Approximately 50% of cases of phenylketonuria effectiveness of the medication. Those patients who are performance may always lag, and permanent damage
respond to the medication tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4, helped may potentially be able to increase the amount may be sustained early in the course of the disease. Only
sapropterin). BH4 has been found to help metabolize of protein in their diet. mild behavioral improvements have been reported.
excess phenylalanine, and its starting dose and main- During therapy, the skin disease, including discolor- Those children who were diagnosed before the onset
tenance dose are based on patient weight and response ation of the hair and skin as well as dermatitis, disap- of any abnormal symptoms and are maintained on a
to Therapy. Levels of phenylalanine must be measured pears. The abnormal EEG pattern reverts to normal, low-phenylalanine diet do not develop any of the
over a few weeks to months to determine the and the patient’s urine returns to normal. Mental sequelae of the disease.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 217