Page 53 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 53
Plate 2-26 Benign Growths
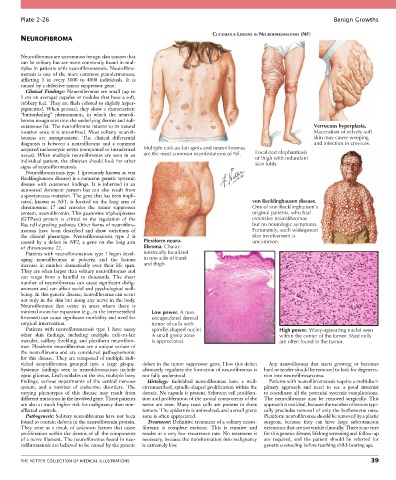
CUTANEOUS LESIONS IN NEUROFIBROMATOSIS (NF)
NEUROFIBROMA
Neurofibromas are uncommon benign skin tumors that
can be solitary but are more commonly found in mul-
tiples in patients with neurofibromatosis. Neurofibro-
matosis is one of the more common genodermatoses,
afflicting 1 in every 3000 to 4000 individuals. It is
caused by a defective tumor suppressor gene.
Clinical Findings: Neurofibromas are small (up to
1 cm on average) papules or nodules that have a soft,
rubbery feel. They are flesh colored to slightly hyper-
pigmented. When pressed, they show a characteristic
“buttonholing” phenomenon, in which the neurofi-
broma invaginates into the underlying dermis and sub-
cutaneous fat. The neurofibroma returns to its natural Verrucous hyperplasia.
location once it is unconfined. Most solitary neurofi- Maceration of velvety-soft
bromas are asymptomatic. The clinical differential skin may cause weeping
diagnosis is between a neurofibroma and a common and infection in crevices.
acquired melanocytic nevus (compound or intradermal Multiple café-au-lait spots and neurofibromas Localized elephantiasis
nevus). When multiple neurofibromas are seen in an are the most common manifestations of NF. of thigh with redundant
individual patient, the clinician should look for other skin folds
signs of neurofibromatosis.
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (previously known as von
Recklinghausen disease) is a common genetic systemic
disease with cutaneous findings. It is inherited in an
autosomal dominant pattern but can also result from
a spontaneous mutation. The gene that has been impli-
cated, known as NF1, is located on the long arm of von Recklinghausen disease.
chromosome 17 and encodes the tumor suppressor One of von Recklinghausen’s
protein, neuro fibromin. This guanosine triphosphatase original patients, who had
(GTPase) protein is critical in the regulation of the extensive neurofibromas
Ras cell signaling pathway. Other forms of neurofibro- but no neurologic symptoms.
matosis have been described and show variations of Fortunately, such widespread
the clinical phenotype. Neurofibromatosis type 2 is skin involvement is
caused by a defect in NF2, a gene on the long arm Plexiform neuro- uncommon.
of chromosome 22. fibroma. Charac-
Patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 begin devel- teristically localized
oping neurofibromas at puberty, and the lesions to one side of trunk
increase in number dramatically over their life span. and thigh
They are often larger than solitary neurofibromas and
can range from a handful to thousands. The sheer
number of neurofibromas can cause significant disfig-
urement and can affect social and psychological well-
being. In this genetic disease, neurofibromas can occur
not only in the skin but along any nerve in the body.
Neurofibromas that occur in areas where there is
minimal room for expansion (e.g., in the intervertebral Low power. A non-
foramen) can cause significant morbidity and need for encapsulated dermal
surgical intervention. tumor of cells with
Patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 have many spindle-shaped nuclei. High power. Wavy-appearing nuclei seen
other skin findings, including multiple café-au-lait A small grenz zone within the center of the tumor. Mast cells
macules, axillary freckling, and plexiform neurofibro- is appreciated. are often found in the tumor.
mas. Plexiform neurofibromas are a unique variant of
the neurofibroma and are considered pathognomonic
for this disease. They are composed of multiple indi-
vidual neurofibromas grouped into a large plaque. defect in the tumor suppressor gene. How this defect Any neurofibroma that starts growing or becomes
Systemic findings seen in neurofibromatosis include ultimately regulates the formation of neurofibromas is hard or tender should be removed to look for degenera-
optic gliomas, Lisch nodules on the iris, multiple bony not fully understood. tion into neurofibrosarcoma.
findings, various impairments of the central nervous Histology: Individual neurofibromas have a well- Patients with neurofibromatosis require a multidisci-
system, and a number of endocrine disorders. The circumscribed, spindle-shaped proliferation within the plinary approach and need to see a good internist
varying phenotypes of this disease may result from dermis. No capsule is present. Schwann cell prolifera- to coordinate all the potential systemic complications.
different mutations in the involved gene. These patients tion and proliferation of the axonal components of the The neurofibromas may be removed surgically. This
are also at much higher risk for malignancy than non- nerve are seen. Many mast cells are present in these approach is not ideal, because the number of lesions typi-
afflicted controls. tumors. The epidermis is uninvolved, and a small grenz cally precludes removal of only the bothersome ones.
Pathogenesis: Solitary neurofibromas have not been zone is often appreciated. Plexiform neurofibromas should be removed by a plastic
found to contain defects in the neurofibromin protein. Treatment: Definitive treatment of a solitary neuro- surgeon, because they can have large subcutaneous
They arise as a result of unknown factors that cause fibroma is complete excision. This is curative and extensions that are not visible clinically. There is no cure
proliferation within the dermis of all the components results in a very low recurrence rate. No treatment is for this genetic disease; lifelong screening and follow-up
of a nerve filament. The neurofibromas found in neu- necessary, because the transformation into malignancy are required, and the patient should be referred for
rofibromatosis are believed to be caused by the genetic is extremely low. genetic counseling before reaching child-bearing age.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 39