Page 54 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 54
Plate 2-27 Integumentary System
Pedunculated
NEVUS LIPOMATOSUS lesion. These
SUPERFICIALIS tumors are
soft, typically
asymptomatic,
Nevus lipomatosus superficialis is a not-uncommon and removed
benign skin growth that is considered to be a hamarto- for cosmetic
matous proliferation of adipose tissue located in the purposes or
dermis. It was originally named nevus lipomatosus because of
cutaneous superficialis of Hoffman-Zurhelle. There chronic
are no known systemic associations with this benign irritation.
skin growth, and no inheritance pattern has been
described.
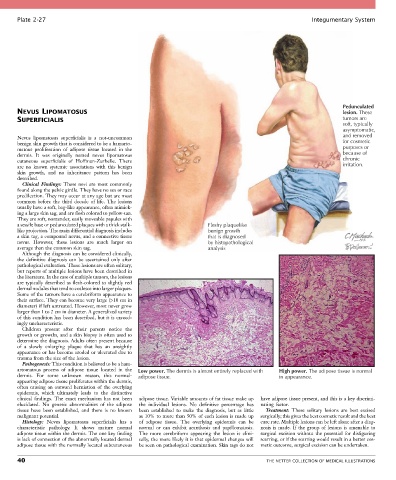
Clinical Findings: These nevi are most commonly
found along the pelvic girdle. They have no sex or race
predilection. They may occur at any age but are most
common before the third decade of life. The lesions
usually have a soft, bag-like appearance, often mimick-
ing a large skin tag, and are flesh colored to yellow-tan.
They are soft, nontender, easily moveable papules with
a sessile base or pedunculated plaques with a thick stalk- Fleshy plaquelike
like projection. The main differential diagnosis includes benign growth
a skin tag, a compound nevus, and a connective tissue that is diagnosed
nevus. However, these lesions are much larger on by histopathological
average than the common skin tag. analysis
Although the diagnosis can be considered clinically,
the definitive diagnosis can be ascertained only after
pathological evaluation. These lesions are often solitary,
but reports of multiple lesions have been described in
the literature. In the case of multiple tumors, the lesions
are typically described as flesh-colored to slightly red
dermal nodules that tend to coalesce into larger plaques.
Some of the tumors have a cerebriform appearance to
their surface. They can become very large (>10 cm in
diameter) if left untreated. However, most never grow
larger than 1 to 2 cm in diameter. A generalized variety
of this condition has been described, but it is exceed-
ingly uncharacteristic.
Children present after their parents notice the
growth or growths, and a skin biopsy is often used to
determine the diagnosis. Adults often present because
of a slowly enlarging plaque that has an unsightly
appearance or has become eroded or ulcerated due to
trauma from the size of the lesion.
Pathogenesis: This condition is believed to be a ham-
artomatous process of adipose tissue located in the Low power. The dermis is almost entirely replaced with High power. The adipose tissue is normal
dermis. For some unknown reason, this normal- adipose tissue. in appearance.
appearing adipose tissue proliferates within the dermis,
often causing an outward herniation of the overlying
epidermis, which ultimately leads to the distinctive
clinical findings. The exact mechanism has not been adipose tissue. Variable amounts of fat tissue make up have adipose tissue present, and this is a key discrimi-
elucidated. No genetic abnormalities of the adipose the individual lesions. No definitive percentage has nating factor.
tissue have been established, and there is no known been established to make the diagnosis, but as little Treatment: These solitary lesions are best excised
malignant potential. as 10% to more than 50% of each lesion is made up surgically; this gives the best cosmetic result and the best
Histology: Nevus lipomatosus superficialis has a of adipose tissue. The overlying epidermis can be cure rate. Multiple lesions can be left alone after a diag-
characteristic pathology. It shows mature normal normal or can exhibit acanthosis and papillomatosis. nosis is made. If the group of lesions is amenable to
adipose tissue within the dermis. The one key finding The more cerebriform appearing the lesion is clini- surgical excision without the potential for disfiguring
is lack of connection of the abnormally located dermal cally, the more likely it is that epidermal changes will scarring, or if the scarring would result in a better cos-
adipose tissue with the normally located subcutaneous be seen on pathological examination. Skin tags do not metic outcome, surgical excision can be undertaken.
40 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS