Page 81 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 81
Plate 3-16 Malignant Growths
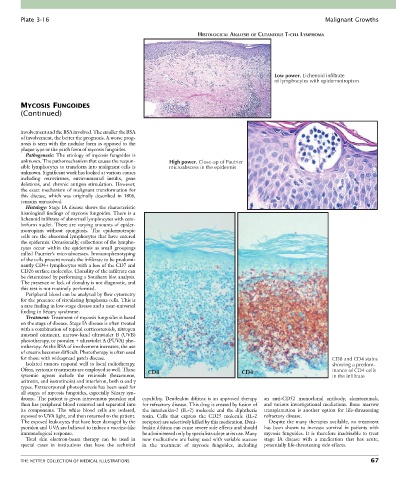
HISTOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF CUTANEOUS T-CELL LYMPHOMA
Low power. Lichenoid infiltrate
of lymphocytes with epidermotropism
MYCOSIS FUNGOIDES
(Continued)
involvement and the BSA involved. The smaller the BSA
of involvement, the better the prognosis. A worse prog-
nosis is seen with the nodular form as opposed to the
plaque type or the patch form of mycosis fungoides.
Pathogenesis: The etiology of mycosis fungoides is
unknown. The pathomechanism that causes the respon- High power. Close-up of Pautrier
sible lymphocytes to transform into malignant cells is microabscess in the epidermis
unknown. Significant work has looked at various causes
including retroviruses, environmental insults, gene
deletions, and chronic antigen stimulation. However,
the exact mechanism of malignant transformation for
this disease, which was originally described in 1806,
remains unresolved.
Histology: Stage IA disease shows the characteristic
histological findings of mycosis fungoides. There is a
lichenoid infiltrate of abnormal lymphocytes with cere-
briform nuclei. There are varying amounts of epider-
motropism without spongiosis. The epidermotropic
cells are the abnormal lymphocytes that have entered
the epidermis. Occasionally, collections of the lympho-
cytes occur within the epidermis as small groupings
called Pautrier’s microabscesses. Immunophenotyping
of the cells present reveals the infiltrate to be predomi-
nantly CD4+ lymphocytes with a loss of the CD7 and
CD26 surface molecules. Clonality of the infiltrate can
be determined by performing a Southern blot analysis.
The presence or lack of clonality is not diagnostic, and
this test is not routinely performed.
Peripheral blood can be analyzed by flow cytometry
for the presence of circulating lymphoma cells. This is
a rare finding in low-stage disease and a near-universal
finding in Sézary syndrome.
Treatment: Treatment of mycosis fungoides is based
on the stage of disease. Stage IA disease is often treated
with a combination of topical corticosteroids, nitrogen
mustard ointment, narrow-band ultraviolet B (UVB)
phototherapy, or psoralen + ultraviolet A (PUVA) pho-
totherapy. As the BSA of involvement increases, the use
of creams becomes difficult. Phototherapy is often used
for those with widespread patch disease. CD8 and CD4 stains
Isolated tumors respond well to local radiotherapy. showing a predom-
Often, systemic treatments are employed as well. These CD8 CD4 inance of CD4 cells
systemic agents include the retinoids (bexarotene, in the infiltrate
acitretin, and isotretinoin) and interferon, both α and γ
types. Extracorporeal photophoresis has been used for
all stages of mycosis fungoides, especially Sézary syn-
drome. The patient is given intravenous psoralen and capability. Denileukin diftitox is an approved therapy an anti-CD52 monoclonal antibody, alemtuzumab,
then has peripheral blood removed and separated into for refractory disease. This drug is created by fusion of and various investigational mediations. Bone marrow
its components. The white blood cells are isolated, the interleukin-2 (IL-2) molecule and the diphtheria transplantation is another option for life-threatening
exposed to UVA light, and then returned to the patient. toxin. Cells that express the CD25 molecule (IL-2 refractory disease.
The exposed leukocytes that have been damaged by the receptor) are selectively killed by this medication. Deni- Despite the many therapies available, no treatment
psoralen and UVA are believed to induce a vaccine-like leukin diftitox can cause severe side effects and should has been shown to increase survival in patients with
immunological response. be administered only by specialists adept at its use. Many mycosis fungoides. It is therefore inadvisable to treat
Total skin electron-beam therapy can be used in new medications are being used with variable success stage IA disease with a medication that has acute,
special cases in institutions that have the technical in the treatment of mycosis fungoides, including potentially life-threatening side effects.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 67