Page 79 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 79
Plate 3-14 Malignant Growths
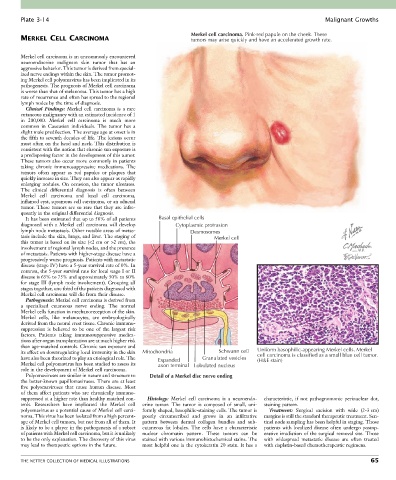
Merkel cell carcinoma. Pink-red papule on the cheek. These
MERKEL CELL CARCINOMA tumors may arise quickly and have an accelerated growth rate.
Merkel cell carcinoma is an uncommonly encountered
neuroendocrine malignant skin tumor that has an
aggressive behavior. This tumor is derived from special-
ized nerve endings within the skin. The tumor promot-
ing Merkel cell polyomavirus has been implicated in its
pathogenesis. The prognosis of Merkel cell carcinoma
is worse than that of melanoma. This tumor has a high
rate of recurrence and often has spread to the regional
lymph nodes by the time of diagnosis.
Clinical Findings: Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare
cutaneous malignancy with an estimated incidence of 1
in 200,000. Merkel cell carcinoma is much more
common in Caucasian individuals. The tumor has a
slight male predilection. The average age at onset is in
the fifth to seventh decades of life. The lesions occur
most often on the head and neck. This distribution is
consistent with the notion that chronic sun exposure is
a predisposing factor in the development of this tumor.
These tumors also occur more commonly in patients
taking chronic immunosuppressive medications. The
tumors often appear as red papules or plaques that
quickly increase in size. They can also appear as rapidly
enlarging nodules. On occasion, the tumor ulcerates.
The clinical differential diagnosis is often between
Merkel cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma,
inflamed cyst, squamous cell carcinoma, or an adnexal
tumor. These tumors are so rare that they are infre-
quently in the original differential diagnosis.
It has been estimated that up to 50% of all patients Basal epithelial cells
diagnosed with a Merkel cell carcinoma will develop Cytoplasmic protrusion
lymph node metastasis. Other notable areas of metas- Desmosomes
tasis include the skin, lungs, and liver. The staging of Merkel cell
this tumor is based on its size (<2 cm or >2 cm), the
involvement of regional lymph nodes, and the presence
of metastasis. Patients with higher-stage disease have a
progressively worse prognosis. Patients with metastatic
disease (stage IV) have a 5-year survival rate of 0%. In
contrast, the 5-year survival rate for local stage I or II
disease is 65% to 75% and approximately 50% to 60%
for stage III (lymph node involvement). Grouping all
stages together, one third of the patients diagnosed with
Merkel cell carcinoma will die from their disease.
Pathogenesis: Merkel cell carcinoma is derived from
a specialized cutaneous nerve ending. The normal
Merkel cells function in mechanoreception of the skin.
Merkel cells, like melanocytes, are embryologically
derived from the neural crest tissue. Chronic immuno-
suppression is believed to be one of the largest risk
factors. Patients taking immunosuppressive medica-
tions after organ transplantation are at much higher risk
than age-matched controls. Chronic sun exposure and
its effect on downregulating local immunity in the skin Mitochondria Schwann cell Uniform basophilic-appearing Merkel cells. Merkel
cell carcinoma is classified as a small blue cell tumor.
have also been theorized to play an etiological role. The Expanded Granulated vesicles (H&E stain)
Merkel cell polyomavirus has been studied to assess its axon terminal Lobulated nucleus
role in the development of Merkel cell carcinoma.
Polyomaviruses are similar in nature and structure to Detail of a Merkel disc nerve ending
the better-known papillomaviruses. There are at least
five polyomaviruses that cause human disease. Most
of them affect patients who are chronically immuno-
suppressed at a higher rate than healthy matched con- Histology: Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendo- characteristic, if not pathognomonic perinuclear dot,
trols. Researchers have implicated the Merkel cell crine tumor. The tumor is composed of small, uni- staining pattern.
polyomavirus as a potential cause of Merkel cell carci- formly shaped, basophilic-staining cells. The tumor is Treatment: Surgical excision with wide (2-3 cm)
noma. This virus has been isolated from a high percent- poorly circumscribed and grows in an infiltrative margins is still the standard therapeutic treatment. Sen-
age of Merkel cell tumors, but not from all of them. It pattern between dermal collagen bundles and sub- tinel node sampling has been helpful in staging. Those
is likely to be a player in the pathogenesis of a subset cutaneous fat lobules. The cells have a characteristic patients with localized disease often undergo postop-
of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma, but it is unlikely nuclear chromatin pattern. These tumors can be erative irradiation of the surgical removal site. Those
to be the only explanation. The discovery of this virus stained with various immunohistochemical stains. The with widespread metastatic disease are often treated
may lead to therapeutic options in the future. most helpful one is the cytokeratin 20 stain. It has a with cisplatin-based chemotherapeutic regimens.
THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS 65