Page 82 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 82
Plate 3-17 Integumentary System
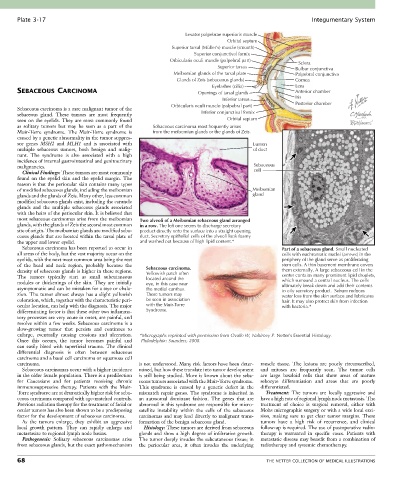
Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
Orbital septum
Superior tarsal (Müller’s) muscle (smooth)
Superior conjunctival fornix
Orbicularis oculi muscle (palpebral part) Sclera
Superior tarsus Bulbar conjunctiva
Meibomian glands of the tarsal plate Palpebral conjunctiva
Glands of Zeis (sebaceous glands) Cornea
Eyelashes (cilia) Lens
SEBACEOUS CARCINOMA Openings of tarsal glands Anterior chamber
Inferior tarsus Iris
Orbicularis oculi muscle (palpebral part) Posterior chamber
Sebaceous carcinoma is a rare malignant tumor of the
sebaceous gland. These tumors are most frequently Inferior conjunctival fornix
seen on the eyelids. They are most commonly found Orbital septum
as solitary tumors but may be seen as a part of the Sebaceous carcinoma most frequently arises
Muir-Torre syndrome. The Muir-Torre syndrome is from the meibomian glands or the glands of Zeis.
caused by a genetic abnormality in the tumor suppres-
sor genes MSH2 and MLH1 and is associated with Lumen
multiple sebaceous tumors, both benign and malig- of duct
nant. The syndrome is also associated with a high
incidence of internal gastrointestinal and genitourinary
malignancies. Sebaceous
Clinical Findings: These tumors are most commonly cell
found on the eyelid skin and the eyelid margin. The
reason is that the periocular skin contains many types
of modified sebaceous glands, including the meibomian Meibomian
glands and the glands of Zeis. Many other, less common gland
modified sebaceous glands exist, including the caruncle
glands and the multiple sebaceous glands associated
with the hairs of the periocular skin. It is believed that
most sebaceous carcinomas arise from the meibomian Two alveoli of a Meibomian sebaceous gland arranged
glands, with the glands of Zeis the second most common in a row. The left one seems to discharge secretory
site of origin. The meibomian glands are modified seba- product directly onto the surface into a straight opening
ceous glands that are located within the tarsal plate of duct. Secretory epithelial cells of the alveoli look foamy
the upper and lower eyelid. and washed out because of high lipid content.*
Sebaceous carcinoma has been reported to occur in Part of a sebaceous gland. Small nucleated
all areas of the body, but the vast majority occur on the cells with euchromatic nuclei (arrows) in the
eyelids, with the next most common area being the rest periphery of the gland serve as proliferating
of the head and neck region, probably because the stem cells. A thin basement membrane covers
density of sebaceous glands is higher in these regions. Sebaceous carcinoma. them externally. A large sebaceous cell in the
Yellowish patch often
The tumors typically start as small subcutaneous located around the center contains many prominent lipid droplets,
nodules or thickenings of the skin. They are initially eye, in this case near which surround a central nucleus. The cells
asymptomatic and can be mistaken for a stye or chala- the medial canthus. ultimately break down and add their contents
to oily secretory product. Sebum reduces
zion. The tumor almost always has a slight yellowish These tumors may water loss from the skin surface and lubricates
coloration, which, together with the characteristic peri- be seen in association hair. It may also protect skin from infection
ocular location, can help with the diagnosis. The major with the Muir-Torre with bacteria.*
differentiating factor is that these other two inflamma- Syndrome.
tory processes are very acute in onset, are painful, and
resolve within a few weeks. Sebaceous carcinoma is a
slow-growing tumor that persists and continues to
enlarge, eventually causing erosions and ulceration. *Micrographs reprinted with permission from Ovalle W, Nahirney P. Netter’s Essential Histology.
Once this occurs, the tumor becomes painful and Philadelphia: Saunders, 2008.
can easily bleed with superficial trauma. The clinical
differential diagnosis is often between sebaceous
carcinoma and a basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell
carcinoma. is not understood. Many risk factors have been deter- muscle tissue. The lesions are poorly circumscribed,
Sebaceous carcinomas occur with a higher incidence mined, but how these translate into tumor development and mitoses are frequently seen. The tumor cells
in the older female population. There is a predilection is still being studied. More is known about the seba- are large basaloid cells that show areas of mature
for Caucasians and for patients receiving chronic ceous tumors associated with the Muir-Torre syndrome. sebocyte differentiation and areas that are poorly
immunosuppressive therapy. Patients with the Muir- This syndrome is caused by a genetic defect in the differentiated.
Torre syndrome are at dramatically higher risk for seba- mismatch repair genes. The syndrome is inherited in Treatment: The tumors are locally aggressive and
ceous carcinoma compared with age-matched controls. an autosomal dominant fashion. The genes that are have a high rate of regional lymph node metastasis. The
Previous radiation therapy for the treatment of facial or abnormal in this syndrome are responsible for micro- treatment of choice is surgical removal, either with
ocular tumors has also been shown to be a predisposing satellite instability within the cells of the sebaceous Mohs micrographic surgery or with a wide local exci-
factor for the development of sebaceous carcinoma. carcinomas and may lead directly to malignant trans- sion, making sure to get clear tumor margins. These
As the tumors enlarge, they exhibit an aggressive formation of the benign sebaceous gland. tumors have a high risk of recurrence, and clinical
local growth pattern. They can rapidly enlarge and Histology: These tumors are derived from sebaceous follow-up is required. The use of postoperative radio-
metastasize to regional lymph node basins. glands and show a high degree of infiltrative growth. therapy is warranted in specific cases. Patients with
Pathogenesis: Solitary sebaceous carcinomas arise The tumor deeply invades the subcutaneous tissue; in metastatic disease may benefit from a combination of
from sebaceous glands, but the exact pathomechanism the periocular area, it often invades the underlying radiotherapy and systemic chemotherapy.
68 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS