Page 78 - The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations - Integumentary System_ Volume 4 ( PDFDrive )
P. 78
Plate 3-13 Integumentary System
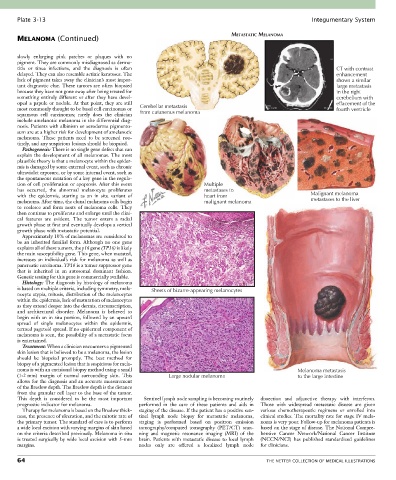
MELANOMA (Continued) METASTATIC MELANOMA
slowly enlarging pink patches or plaques with no
pigment. They are commonly misdiagnosed as derma-
titis or tinea infections, and the diagnosis is often CT with contrast
delayed. They can also resemble actinic keratoses. The enhancement
lack of pigment takes away the clinician’s most impor- shows a similar
tant diagnostic clue. These tumors are often biopsied large metastasis
because they have not gone away after being treated for in the right
something entirely different or after they have devel- cerebellum with
oped a papule or nodule. At that point, they are still effacement of the
most commonly thought to be basal cell carcinomas or Cerebellar metastasis fourth ventricle
squamous cell carcinomas; rarely does the clinician from cutaneous melanoma
include amelanotic melanoma in the differential diag-
nosis. Patients with albinism or xeroderma pigmento-
sum are at a higher risk for development of amelanotic
melanoma. These patients need to be screened rou-
tinely, and any suspicious lesions should be biopsied.
Pathogenesis: There is no single gene defect that can
explain the development of all melanomas. The most
plausible theory is that a melanocyte within the epider-
mis is damaged by some external event, such as chronic
ultraviolet exposure, or by some internal event, such as
the spontaneous mutation of a key gene in the regula-
tion of cell proliferation or apoptosis. After this event Multiple
has occurred, the abnormal melanocyte proliferates metastases to
with the epidermis, starting as an in situ variant of heart from Malignant melanoma
melanoma. After time, the clonal melanoma cells begin malignant melanoma metastases to the liver
to coalesce and form nests of melanoma cells. They
then continue to proliferate and enlarge until the clini-
cal features are evident. The tumor enters a radial
growth phase at first and eventually develops a vertical
growth phase with metastatic potential.
Approximately 10% of melanomas are considered to
be an inherited familial form. Although no one gene
explains all of these tumors, the p16 gene (TP16) is likely
the main susceptibility gene. This gene, when mutated,
increases an individual’s risk for melanoma as well as
pancreatic carcinoma. TP16 is a tumor suppressor gene
that is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion.
Genetic testing for this gene is commercially available.
Histology: The diagnosis by histology of melanoma
is based on multiple criteria, including symmetry, mela- Sheets of bizarre-appearing melanocytes
nocyte atypia, mitosis, distribution of the melanocytes
within the epidermis, lack of maturation of melanocytes
as they extend deeper into the dermis, circumscription,
and architectural disorder. Melanoma is believed to
begin with an in situ portion, followed by an upward
spread of single melanocytes within the epidermis,
termed pagetoid spread. If no epidermal component of
melanoma is seen, the possibility of a metastatic focus
is entertained.
Treatment: When a clinician encounters a pigmented
skin lesion that is believed to be a melanoma, the lesion
should be biopsied promptly. The best method for
biopsy of a pigmented lesion that is suspicious for mela-
noma is with an excisional biopsy method using a small Melanoma metastasis
(1-2 mm) margin of normal surrounding skin. This Large nodular melanoma to the large intestine
allows for the diagnosis and an accurate measurement
of the Breslow depth. The Breslow depth is the distance
from the granular cell layer to the base of the tumor.
This depth is considered to be the most important Sentinel lymph node sampling is becoming routinely dissection and adjunctive therapy with interferon.
prognostic indicator for melanoma. performed in the care of these patients and aids in Those with widespread metastatic disease are given
Therapy for melanoma is based on the Breslow thick- staging of the disease. If the patient has a positive sen- various chemotherapeutic regimens or enrolled into
ness, the presence of ulceration, and the mitotic rate of tinel lymph node biopsy for metastatic melanoma, clinical studies. The mortality rate for stage IV mela-
the primary tumor. The standard of care is to perform staging is performed based on positron emission noma is very poor. Follow-up for melanoma patients is
a wide local excision with varying margins of skin based tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) scan- based on the stage of disease. The National Compre-
on the criteria described previously. Melanoma in situ ning and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the hensive Cancer Network/National Cancer Institute
is treated surgically by wide local excision with 5-mm brain. Patients with metastatic disease to local lymph (NCCN/NCI) has published standardized guidelines
margins. nodes only are offered a localized lymph node for clinicians.
64 THE NETTER COLLECTION OF MEDICAL ILLUSTRATIONS